Hints will display for most wrong answers; explanations for most right answers. You can attempt a question multiple times; it will only be scored correct if you get it right the first time. To see ten new questions, reload the page.
I used the official objectives and sample test to construct these questions, but cannot promise that they accurately reflect what’s on the real test. Some of the sample questions were more convoluted than I could bear to write. See terms of use. See the MTEL Practice Test main page to view questions on a particular topic or to download paper practice tests.
MTEL General Curriculum Mathematics Practice
Question 1 |
A sales companies pays its representatives $2 for each item sold, plus 40% of the price of the item. The rest of the money that the representatives collect goes to the company. All transactions are in cash, and all items cost $4 or more. If the price of an item in dollars is p, which expression represents the amount of money the company collects when the item is sold?
\( \large \dfrac{3}{5}p-2\) Hint: The company gets 3/5=60% of the price, minus the $2 per item. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{5}\left( p-2 \right)\) Hint: This is sensible, but not what the problem states. | |
\( \large \dfrac{2}{5}p+2\) Hint: The company pays the extra $2; it doesn't collect it. | |
\( \large \dfrac{2}{5}p-2\) Hint: This has the company getting 2/5 = 40% of the price of each item, but that's what the representative gets. |
Question 2 |
The letters A, and B represent digits (possibly equal) in the ten digit number x=1,438,152,A3B. For which values of A and B is x divisible by 12, but not by 9?
\( \large A = 0, B = 4\) Hint: Digits add to 31, so not divisible by 3, so not divisible by 12. | |
\( \large A = 7, B = 2\) Hint: Digits add to 36, so divisible by 9. | |
\( \large A = 0, B = 6\) Hint: Digits add to 33, divisible by 3, not 9. Last digits are 36, so divisible by 4, and hence by 12. | |
\( \large A = 4, B = 8\) Hint: Digits add to 39, divisible by 3, not 9. Last digits are 38, so not divisible by 4, so not divisible by 12. |
Question 3 |
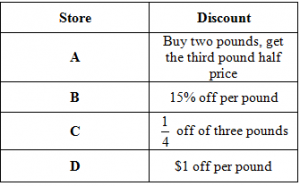
Use the table below to answer the question that follows:
Gordon wants to buy three pounds of nuts. Each of the stores above ordinarily sells the nuts for $4.99 a pound, but is offering a discount this week. At which store can he buy the nuts for the least amount of money?
Store AHint: This would save about $2.50. You can quickly see that D saves more. | |
Store BHint: This saves 15% and C saves 25%. | |
Store C | |
Store DHint: This is about 20% off, which is less of a discount than C. |
Question 4 |
Use the samples of a student's work below to answer the question that follows:
\( \large \dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{4\times 2}{3\times 3}=\dfrac{8}{9}\) \( \large \dfrac{2}{5}\times \dfrac{7}{7}=\dfrac{7\times 2}{5\times 7}=\dfrac{2}{5}\) \( \large \dfrac{7}{6}\times \dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{4\times 7}{6\times 3}=\dfrac{28}{18}=\dfrac{14}{9}\)Which of the following best describes the mathematical validity of the algorithm the student is using?
It is not valid. It never produces the correct answer.Hint: In the middle example,the answer is correct. | |
It is not valid. It produces the correct answer in a few special cases, but it‘s still not a valid algorithm.Hint: Note that this algorithm gives a/b divided by c/d, not a/b x c/d, but some students confuse multiplication and cross-multiplication. If a=0 or if c/d =1, division and multiplication give the same answer. | |
It is valid if the rational numbers in the multiplication problem are in lowest terms.Hint: Lowest terms is irrelevant. | |
It is valid for all rational numbers.Hint: Can't be correct as the first and last examples have the wrong answers. |
Question 5 |
The polygon depicted below is drawn on dot paper, with the dots spaced 1 unit apart. What is the perimeter of the polygon?

\( \large 18+\sqrt{2} \text{ units}\) Hint: Be careful with the Pythagorean Theorem. | |
\( \large 18+2\sqrt{2}\text{ units}\) Hint: There are 13 horizontal or vertical 1 unit segments. The longer diagonal is the hypotenuse of a 3-4-5 right triangle, so its length is 5 units. The shorter diagonal is the hypotenuse of a 45-45-90 right triangle with side 2, so its hypotenuse has length \(2 \sqrt{2}\). | |
\( \large 18 \text{ units}
\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the diagonal segments. | |
\( \large 20 \text{ units}\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the diagonal segments. |
Question 6 |
Below is a portion of a number line.
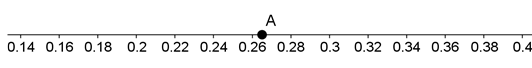
Point A is one-quarter of the distance from 0.26 to 0.28. What number is represented by point A?
\( \large0.26\) Hint: Please reread the question. | |
\( \large0.2625\) Hint: This is one-quarter of the distance between 0.26 and 0.27, which is not what the question asked. | |
\( \large0.265\) | |
\( \large0.27\) Hint: Please read the question more carefully. This answer would be correct if Point A were halfway between the tick marks, but it's not. |
Question 7 |
In which table below is y a function of x?
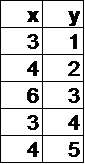 Hint: If x=3, y can have two different values, so it's not a function. | |
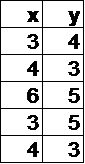 Hint: If x=3, y can have two different values, so it's not a function. | |
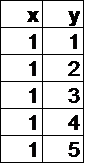 Hint: If x=1, y can have different values, so it's not a function. | |
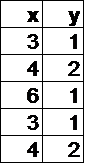 Hint: Each value of x always corresponds to the same value of y. |
Question 8 |
Four children randomly line up, single file. What is the probability that they are in height order, with the shortest child in front? All of the children are different heights.
\( \large \dfrac{1}{4}\) Hint: Try a simpler question with 3 children -- call them big, medium, and small -- and list all the ways they could line up. Then see how to extend your logic to the problem with 4 children. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{256}
\) Hint: Try a simpler question with 3 children -- call them big, medium, and small -- and list all the ways they could line up. Then see how to extend your logic to the problem with 4 children. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{16}\) Hint: Try a simpler question with 3 children -- call them big, medium, and small -- and list all the ways they could line up. Then see how to extend your logic to the problem with 4 children. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{24}\) Hint: The number of ways for the children to line up is \(4!=4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 =24\) -- there are 4 choices for who is first in line, then 3 for who is second, etc. Only one of these lines has the children in the order specified. |
Question 9 |
What is the mathematical name of the three-dimensional polyhedron depicted below?
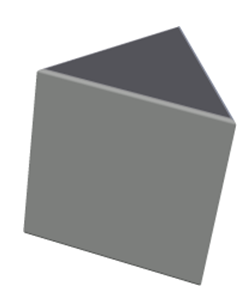
TetrahedronHint: All the faces of a tetrahedron are triangles. | |
Triangular PrismHint: A prism has two congruent, parallel bases, connected by parallelograms (since this is a right prism, the parallelograms are rectangles). | |
Triangular PyramidHint: A pyramid has one base, not two. | |
TrigonHint: A trigon is a triangle (this is not a common term). |
Question 10 |
How many factors does 80 have?
\( \large8\) Hint: Don't forget 1 and 80. | |
\( \large9\) Hint: Only perfect squares have an odd number of factors -- otherwise factors come in pairs. | |
\( \large10\) Hint: 1,2,4,5,8,10,16,20,40,80 | |
\( \large12\) Hint: Did you count a number twice? Include a number that isn't a factor? |
If you found a mistake or have comments on a particular question, please contact me (please copy and paste at least part of the question into the form, as the numbers change depending on how quizzes are displayed). General comments can be left here.