Hints will display for most wrong answers; explanations for most right answers. You can attempt a question multiple times; it will only be scored correct if you get it right the first time.
I used the official objectives and sample test to construct these questions, but cannot promise that they accurately reflect what’s on the real test. Some of the sample questions were more convoluted than I could bear to write. See terms of use. See the MTEL Practice Test main page to view questions on a particular topic or to download paper practice tests.
MTEL General Curriculum Mathematics Practice
Question 1 |
A biology class requires a lab fee, which is a whole number of dollars, and the same amount for all students. On Monday the instructor collected $70 in fees, on Tuesday she collected $126, and on Wednesday she collected $266. What is the largest possible amount the fee could be?
$2Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$7Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$14Hint: This is the greatest common factor of 70, 126, and 266. | |
$70Hint: Not a factor of 126 or 266, so couldn't be correct. |
Question 2 |
AHint: \(\frac{34}{135} \approx \frac{1}{4}\) and \( \frac{53}{86} \approx \frac {2}{3}\). \(\frac {1}{4}\) of \(\frac {2}{3}\) is small and closest to A. | |
BHint: Estimate with simpler fractions. | |
CHint: Estimate with simpler fractions. | |
DHint: Estimate with simpler fractions. |
Question 3 |
The prime factorization of n can be written as n=pqr, where p, q, and r are distinct prime numbers. How many factors does n have, including 1 and itself?
\( \large3\) Hint: 1, p, q, r, and pqr are already 5, so this isn't enough. You might try plugging in p=2, q=3, and r=5 to help with this problem. | |
\( \large5\) Hint: Don't forget pq, etc. You might try plugging in p=2, q=3, and r=5 to help with this problem. | |
\( \large6\) Hint: You might try plugging in p=2, q=3, and r=5 to help with this problem. | |
\( \large8\) Hint: 1, p, q, r, pq, pr, qr, pqr. |
Question 4 |
A publisher prints a series of books with covers made of identical material and using the same thickness of paper for each page. The covers of the book together are 0.4 cm thick, and 125 pieces of the paper used together are 1 cm thick.
The publisher uses a linear function to determine the total thickness, T(n) of a book made with n sheets of paper. What are the slope and intercept of T(n)?
Intercept = 0.4 cm, Slope = 125 cm/pageHint: This would mean that each page of the book was 125 cm thick. | |
Intercept =0.4 cm, Slope = \(\dfrac{1}{125}\)cm/pageHint: The intercept is how thick the book would be with no pages in it. The slope is how much 1 extra page adds to the thickness of the book. | |
Intercept = 125 cm, Slope = 0.4 cmHint: This would mean that with no pages in the book, it would be 125 cm thick. | |
Intercept = \(\dfrac{1}{125}\)cm, Slope = 0.4 pages/cmHint: This would mean that each new page of the book made it 0.4 cm thicker. |
Question 5 |
Which of the numbers below is not equivalent to 4%?
\( \large \dfrac{1}{25}\) Hint: 1/25=4/100, so this is equal to 4% (be sure you read the question correctly). | |
\( \large \dfrac{4}{100}\) Hint: 4/100=4% (be sure you read the question correctly). | |
\( \large 0.4\) Hint: 0.4=40% so this is not equal to 4% | |
\( \large 0.04\) Hint: 0.04=4/100, so this is equal to 4% (be sure you read the question correctly). |
Question 6 |
Four children randomly line up, single file. What is the probability that they are in height order, with the shortest child in front? All of the children are different heights.
\( \large \dfrac{1}{4}\) Hint: Try a simpler question with 3 children -- call them big, medium, and small -- and list all the ways they could line up. Then see how to extend your logic to the problem with 4 children. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{256}
\) Hint: Try a simpler question with 3 children -- call them big, medium, and small -- and list all the ways they could line up. Then see how to extend your logic to the problem with 4 children. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{16}\) Hint: Try a simpler question with 3 children -- call them big, medium, and small -- and list all the ways they could line up. Then see how to extend your logic to the problem with 4 children. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{24}\) Hint: The number of ways for the children to line up is \(4!=4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 =24\) -- there are 4 choices for who is first in line, then 3 for who is second, etc. Only one of these lines has the children in the order specified. |
Question 7 |
The first histogram shows the average life expectancies for women in different countries in Africa in 1998; the second histogram gives similar data for Europe:
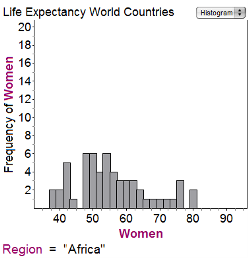
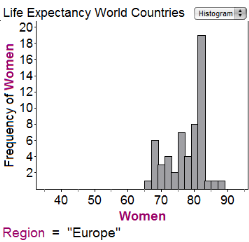
How much bigger is the range of the data for Africa than the range of the data for Europe?
0 yearsHint: Range is the maximum life expectancy minus the minimum life expectancy. | |
12 yearsHint: Are you subtracting frequencies? Range is about values of the data, not frequency. | |
18 yearsHint: It's a little hard to read the graph, but it doesn't matter if you're consistent. It looks like the range for Africa is 80-38= 42 years and for Europe is 88-64 = 24; 42-24=18. | |
42 yearsHint: Read the question more carefully. |
Question 8 |
Which of the following inequalities describes all values of x with \(\large \dfrac{x}{2}\le \dfrac{x}{3}\)?
\( \large x < 0\) Hint: If x =0, then x/2 = x/3, so this answer can't be correct. | |
\( \large x \le 0\) | |
\( \large x > 0\) Hint: If x =0, then x/2 = x/3, so this answer can't be correct. | |
\( \large x \ge 0\) Hint: Try plugging in x = 6. |
Question 9 |
There are six gumballs in a bag — two red and four green. Six children take turns picking a gumball out of the bag without looking. They do not return any gumballs to the bag. What is the probability that the first two children to pick from the bag pick the red gumballs?
\( \large \dfrac{1}{3}\) Hint: This is the probability that the first child picks a red gumball, but not that the first two children pick red gumballs. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{8}\) Hint: Are you adding things that you should be multiplying? | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{9}\) Hint: This would be the probability if the gumballs were returned to the bag. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{15}\) Hint: The probability that the first child picks red is 2/6 = 1/3. Then there are 5 gumballs in the bag, one red, so the probability that the second child picks red is 1/5. Thus 1/5 of the time, after the first child picks red, the second does too, so the probability is 1/5 x 1/3 = 1/15. |
Question 10 |
What is the mathematical name of the three-dimensional polyhedron depicted below?
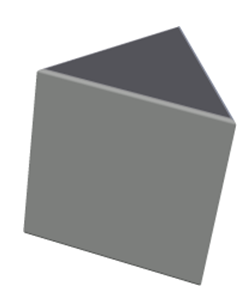
TetrahedronHint: All the faces of a tetrahedron are triangles. | |
Triangular PrismHint: A prism has two congruent, parallel bases, connected by parallelograms (since this is a right prism, the parallelograms are rectangles). | |
Triangular PyramidHint: A pyramid has one base, not two. | |
TrigonHint: A trigon is a triangle (this is not a common term). |
Question 11 |
Taxicab fares in Boston (Spring 2012) are $2.60 for the first \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile or less and $0.40 for each \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile after that.
Let d represent the distance a passenger travels in miles (with \(d>\dfrac{1}{7}\)). Which of the following expressions represents the total fare?
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40d\) Hint: It's 40 cents for 1/7 of a mile, not per mile. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40\dfrac{d}{7}\) Hint: According to this equation, going 7 miles would cost $3; does that make sense? | |
\( \large \$2.20+\$2.80d\) Hint: You can think of the fare as $2.20 to enter the cab, and then $0.40 for each 1/7 of a mile, including the first 1/7 of a mile (or $2.80 per mile).
Alternatively, you pay $2.60 for the first 1/7 of a mile, and then $2.80 per mile for d-1/7 miles. The total is 2.60+2.80(d-1/7) = 2.60+ 2.80d -.40 = 2.20+2.80d. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$2.80d\) Hint: Don't count the first 1/7 of a mile twice. |
Question 12 |
The histogram below shows the number of pairs of footware owned by a group of college students.
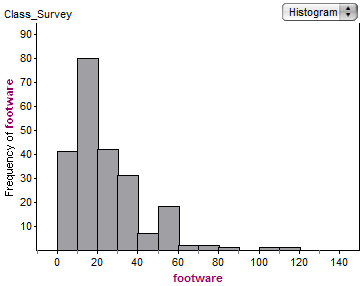
Which of the following statements can be inferred from the graph above?
The median number of pairs of footware owned is between 50 and 60 pairs.Hint: The same number of data points are less than the median as are greater than the median -- but on this histogram, clearly more than half the students own less than 50 pairs of shoes, so the median is less than 50. | |
The mode of the number of pairs of footware owned is 20.Hint: The mode is the most common number of pairs of footwear owned. We can't tell it from this histogram because each bar represents 10 different numbers-- perhaps 8 students each own each number from 10 to 19, but 40 students own exactly 6 pairs of shoes.... or perhaps not.... | |
The mean number of pairs of footware owned is less than the median number of pairs of footware owned.Hint: This is a right skewed distribution, and so the mean is bigger than the median -- the few large values on the right pull up the mean, but have little effect on the median. | |
The median number of pairs of footware owned is between 10 and 20.Hint: There are approximately 230 students represented in this survey, and the 41st through 120th lowest values are between 10 and 20 -- thus the middle value is in that range. |
Question 13 |
Solve for x: \(\large 4-\dfrac{2}{3}x=2x\)
\( \large x=3\) Hint: Try plugging x=3 into the equation. | |
\( \large x=-3\) Hint: Left side is positive, right side is negative when you plug this in for x. | |
\( \large x=\dfrac{3}{2}\) Hint: One way to solve: \(4=\dfrac{2}{3}x+2x\) \(=\dfrac{8}{3}x\).\(x=\dfrac{3 \times 4}{8}=\dfrac{3}{2}\). Another way is to just plug x=3/2 into the equation and see that each side equals 3 -- on a multiple choice test, you almost never have to actually solve for x. | |
\( \large x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\) Hint: Left side is positive, right side is negative when you plug this in for x. |
Question 14 |
The pattern below consists of a row of black squares surrounded by white squares.
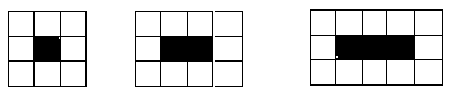
How many white squares would surround a row of 157 black squares?
314Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. | |
317Hint: Are there ever an odd number of white squares? | |
320Hint: One way to see this is that there are 6 tiles on the left and right ends, and the rest of the white tiles are twice the number of black tiles (there are many other ways to look at it too). | |
322Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. |
Question 15 |
The Americans with Disabilties Act (ADA) regulations state that the maximum slope for a wheelchair ramp in new construction is 1:12, although slopes between 1:16 and 1:20 are preferred. The maximum rise for any run is 30 inches. The graph below shows the rise and runs of four different wheelchair ramps. Which ramp is in compliance with the ADA regulations for new construction?
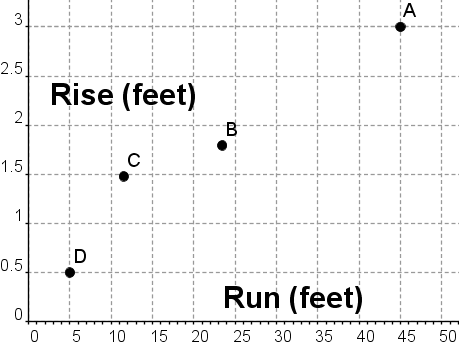
AHint: Rise is more than 30 inches. | |
BHint: Run is almost 24 feet, so rise can be almost 2 feet. | |
CHint: Run is 12 feet, so rise can be at most 1 foot. | |
DHint: Slope is 1:10 -- too steep. |
Question 16 |
The equation \( \large F=\frac{9}{5}C+32\) is used to convert a temperature measured in Celsius to the equivalent Farentheit temperature.
A patient's temperature increased by 1.5° Celcius. By how many degrees Fahrenheit did her temperature increase?
1.5°Hint: Celsius and Fahrenheit don't increase at the same rate. | |
1.8°Hint: That's how much the Fahrenheit temp increases when the Celsius temp goes up by 1 degree. | |
2.7°Hint: Each degree increase in Celsius corresponds to a \(\dfrac{9}{5}=1.8\) degree increase in Fahrenheit. Thus the increase is 1.8+0.9=2.7. | |
Not enough information.Hint: A linear equation has constant slope, which means that every increase of the same amount in one variable, gives a constant increase in the other variable. It doesn't matter what temperature the patient started out at. |
Question 17 |
How many factors does 80 have?
\( \large8\) Hint: Don't forget 1 and 80. | |
\( \large9\) Hint: Only perfect squares have an odd number of factors -- otherwise factors come in pairs. | |
\( \large10\) Hint: 1,2,4,5,8,10,16,20,40,80 | |
\( \large12\) Hint: Did you count a number twice? Include a number that isn't a factor? |
Question 18 |
Exactly one of the numbers below is a prime number. Which one is it?
\( \large511 \) Hint: Divisible by 7. | |
\( \large517\) Hint: Divisible by 11. | |
\( \large519\) Hint: Divisible by 3. | |
\( \large521\) |
Question 19 |
Use the problem below to answer the question that follows:
T shirts are on sale for 20% off. Tasha paid $8.73 for a shirt. What is the regular price of the shirt? There is no tax on clothing purchases under $175.
Let p represent the regular price of these t-shirt. Which of the following equations is correct?
\( \large 0.8p=\$8.73\) Hint: 80% of the regular price = $8.73. | |
\( \large \$8.73+0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice c. | |
\( \large 1.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice b. | |
\( \large p-0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: Subtract p from both sides of this equation, and you have -.2 x 8.73 =0. |
Question 20 |
The following story situations model \( 12\div 3\):
I) Jack has 12 cookies, which he wants to share equally between himself and two friends. How many cookies does each person get?
II) Trent has 12 cookies, which he wants to put into bags of 3 cookies each. How many bags can he make?
III) Cicely has $12. Cookies cost $3 each. How many cookies can she buy?
Which of these questions illustrate the same model of division, either partitive (partioning) or measurement (quotative)?
I and II | |
I and III | |
II and IIIHint: Problem I is partitive (or partitioning or sharing) -- we put 12 objects into 3 groups. Problems II and III are quotative (or measurement) -- we put 12 objects in groups of 3. | |
All three problems model the same meaning of division |
|
List |
If you found a mistake or have comments on a particular question, please contact me (please copy and paste at least part of the question into the form, as the numbers change depending on how quizzes are displayed). General comments can be left here.
