Hints will display for most wrong answers; explanations for most right answers. You can attempt a question multiple times; it will only be scored correct if you get it right the first time.
I used the official objectives and sample test to construct these questions, but cannot promise that they accurately reflect what’s on the real test. Some of the sample questions were more convoluted than I could bear to write. See terms of use. See the MTEL Practice Test main page to view questions on a particular topic or to download paper practice tests.
MTEL General Curriculum Mathematics Practice
Question 1 |
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
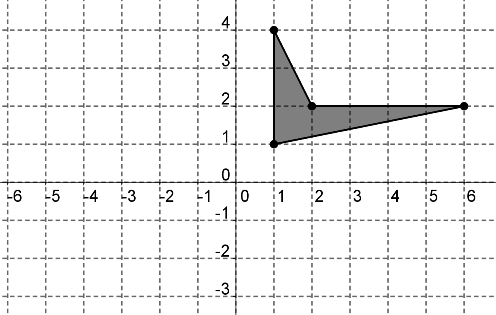
If the polygon shown above is reflected about the y axis and then rotated 90 degrees clockwise about the origin, which of the following graphs is the result?
 Hint: Try following the point (1,4) to see where it goes after each transformation. | |
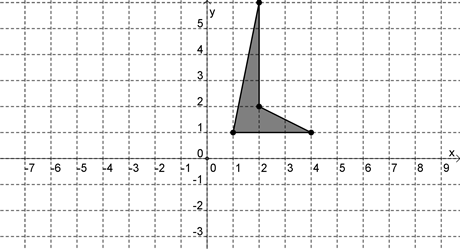 | |
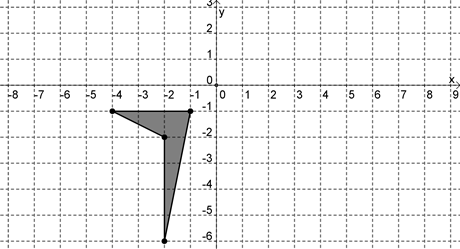
Hint: Make sure you're reflecting in the correct axis. | |
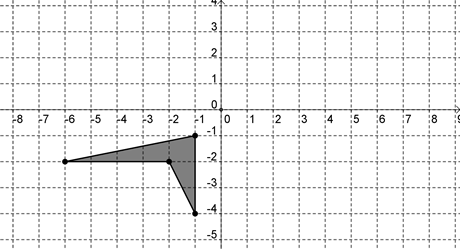 Hint: Make sure you're rotating the correct direction. |
Question 2 |
The letters A, B, and C represent digits (possibly equal) in the twelve digit number x=111,111,111,ABC. For which values of A, B, and C is x divisible by 40?
\( \large A = 3, B = 2, C=0\) Hint: Note that it doesn't matter what the first 9 digits are, since 1000 is divisible by 40, so DEF,GHI,JKL,000 is divisible by 40 - we need to check the last 3. | |
\( \large A = 0, B = 0, C=4\) Hint: Not divisible by 10, since it doesn't end in 0. | |
\( \large A = 4, B = 2, C=0\) Hint: Divisible by 10 and by 4, but not by 40, as it's not divisible by 8. Look at 40 as the product of powers of primes -- 8 x 5, and check each. To check 8, either check whether 420 is divisible by 8, or take ones place + twice tens place + 4 * hundreds place = 18, which is not divisible by 8. | |
\( \large A =1, B=0, C=0\) Hint: Divisible by 10 and by 4, but not by 40, as it's not divisible by 8. Look at 40 as the product of powers of primes -- 8 x 5, and check each. To check 8, either check whether 100 is divisible by 8, or take ones place + twice tens place + 4 * hundreds place = 4, which is not divisible by 8. |
Question 3 |
The Venn Diagram below gives data on the number of seniors, athletes, and vegetarians in the student body at a college:
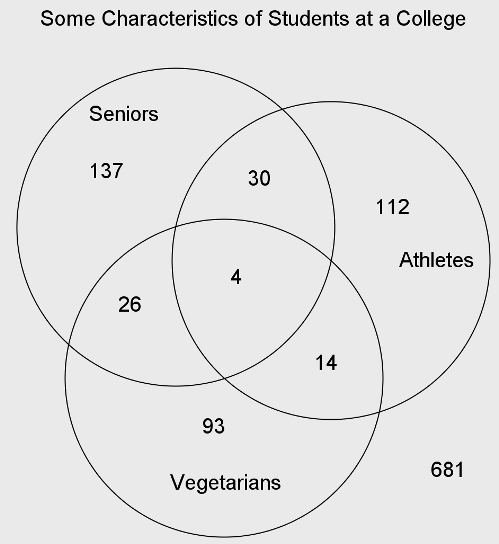
How many students at the college are seniors who are not vegetarians?
\( \large 137\) Hint: Doesn't include the senior athletes who are not vegetarians. | |
\( \large 167\) | |
\( \large 197\) Hint: That's all seniors, including vegetarians. | |
\( \large 279\) Hint: Includes all athletes who are not vegetarians, some of whom are not seniors. |
Question 4 |
Below is a portion of a number line:
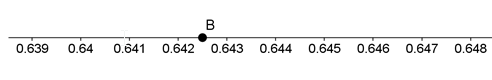
Point B is halfway between two tick marks. What number is represented by Point B?
\( \large 0.645\) Hint: That point is marked on the line, to the right. | |
\( \large 0.6421\) Hint: That point is to the left of point B. | |
\( \large 0.6422\) Hint: That point is to the left of point B. | |
\( \large 0.6425\) |
Question 5 |
What is the perimeter of a right triangle with legs of lengths x and 2x?
\( \large 6x\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem. | |
\( \large 3x+5{{x}^{2}}\) Hint: Don't forget to take square roots when you use the Pythagorean Theorem. | |
\( \large 3x+\sqrt{5}{{x}^{2}}\) Hint: \(\sqrt {5 x^2}\) is not \(\sqrt {5}x^2\). | |
\( \large 3x+\sqrt{5}{{x}^{{}}}\) Hint: To find the hypotenuse, h, use the Pythagorean Theorem: \(x^2+(2x)^2=h^2.\) \(5x^2=h^2,h=\sqrt{5}x\). The perimeter is this plus x plus 2x. |
Question 6 |
AHint: \(\frac{34}{135} \approx \frac{1}{4}\) and \( \frac{53}{86} \approx \frac {2}{3}\). \(\frac {1}{4}\) of \(\frac {2}{3}\) is small and closest to A. | |
BHint: Estimate with simpler fractions. | |
CHint: Estimate with simpler fractions. | |
DHint: Estimate with simpler fractions. |
Question 7 |
Which of the following values of x satisfies the inequality \( \large \left| {{(x+2)}^{3}} \right|<3?\)
\( \large x=-3\) Hint: \( \left| {{(-3+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {(-1)}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | -1 \right |=1 \) . | |
\( \large x=0\) Hint: \( \left| {{(0+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {2}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | 8 \right | \) =\( 8\) | |
\( \large x=-4\) Hint: \( \left| {{(-4+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {(-2)}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | -8 \right | \) =\( 8\) | |
\( \large x=1\) Hint: \( \left| {{(1+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {3}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | 27 \right | \) = \(27\) |
Question 8 |
Below are four inputs and outputs for a function machine representing the function A:
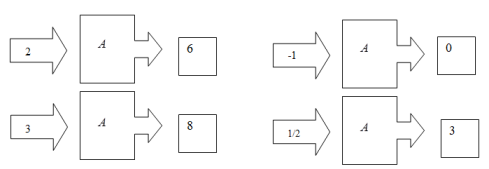
Which of the following equations could also represent A for the values shown?
\( \large A(n)=n+4\) Hint: For a question like this, you don't have to find the equation yourself, you can just try plugging the function machine inputs into the equation, and see if any values come out wrong. With this equation n= -1 would output 3, not 0 as the machine does. | |
\( \large A(n)=n+2\) Hint: For a question like this, you don't have to find the equation yourself, you can just try plugging the function machine inputs into the equation, and see if any values come out wrong. With this equation n= 2 would output 4, not 6 as the machine does. | |
\( \large A(n)=2n+2\) Hint: Simply plug in each of the four function machine input values, and see that the equation produces the correct output, e.g. A(2)=6, A(-1)=0, etc. | |
\( \large A(n)=2\left( n+2 \right)\) Hint: For a question like this, you don't have to find the equation yourself, you can just try plugging the function machine inputs into the equation, and see if any values come out wrong. With this equation n= 2 would output 8, not 6 as the machine does. |
Question 9 |
Which of the graphs below represent functions?
I.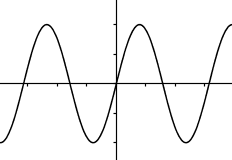 II.
II. 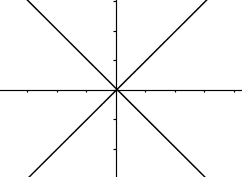 III.
III. 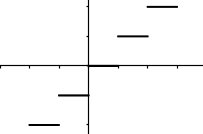 IV.
IV. 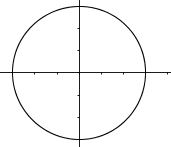
I and IV only.Hint: There are vertical lines that go through 2 points in IV . | |
I and III only.Hint: Even though III is not continuous, it's still a function (assuming that vertical lines between the "steps" do not go through 2 points). | |
II and III only.Hint: Learn about the vertical line test. | |
I, II, and IV only.Hint: There are vertical lines that go through 2 points in II. |
Question 10 |
The prime factorization of n can be written as n=pqr, where p, q, and r are distinct prime numbers. How many factors does n have, including 1 and itself?
\( \large3\) Hint: 1, p, q, r, and pqr are already 5, so this isn't enough. You might try plugging in p=2, q=3, and r=5 to help with this problem. | |
\( \large5\) Hint: Don't forget pq, etc. You might try plugging in p=2, q=3, and r=5 to help with this problem. | |
\( \large6\) Hint: You might try plugging in p=2, q=3, and r=5 to help with this problem. | |
\( \large8\) Hint: 1, p, q, r, pq, pr, qr, pqr. |
Question 11 |
Which of the following is equivalent to \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}?\)
\( \large \dfrac{7}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2}\) Hint: Addition and subtraction are of equal priority in the order of operations -- do them left to right. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{4}\) Hint: \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}+-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. |
Question 12 |
A biology class requires a lab fee, which is a whole number of dollars, and the same amount for all students. On Monday the instructor collected $70 in fees, on Tuesday she collected $126, and on Wednesday she collected $266. What is the largest possible amount the fee could be?
$2Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$7Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$14Hint: This is the greatest common factor of 70, 126, and 266. | |
$70Hint: Not a factor of 126 or 266, so couldn't be correct. |
Question 13 |
Which of the lines depicted below is a graph of \( \large y=2x-5\)?
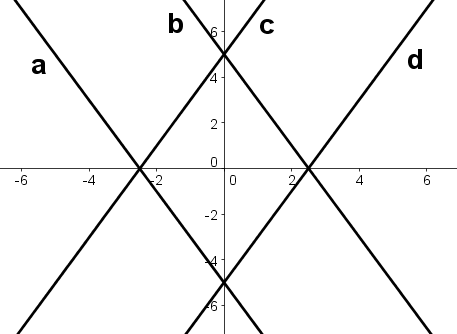
aHint: The slope of line a is negative. | |
bHint: Wrong slope and wrong intercept. | |
cHint: The intercept of line c is positive. | |
dHint: Slope is 2 -- for every increase of 1 in x, y increases by 2. Intercept is -5 -- the point (0,-5) is on the line. |
Question 14 |
The pattern below consists of a row of black squares surrounded by white squares.
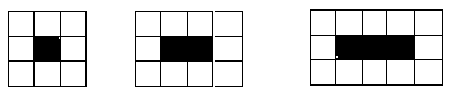
How many white squares would surround a row of 157 black squares?
314Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. | |
317Hint: Are there ever an odd number of white squares? | |
320Hint: One way to see this is that there are 6 tiles on the left and right ends, and the rest of the white tiles are twice the number of black tiles (there are many other ways to look at it too). | |
322Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. |
Question 15 |
The speed of sound in dry air at 68 degrees F is 343.2 meters per second. Which of the expressions below could be used to compute the number of kilometers that a sound wave travels in 10 minutes (in dry air at 68 degrees F)?
\( \large 343.2\times 60\times 10\) Hint: In kilometers, not meters. | |
\( \large 343.2\times 60\times 10\times \dfrac{1}{1000}\) Hint: Units are meters/sec \(\times\) seconds/minute \(\times\) minutes \(\times\) kilometers/meter, and the answer is in kilometers. | |
\( \large 343.2\times \dfrac{1}{60}\times 10\) Hint: Include units and make sure answer is in kilometers. | |
\( \large 343.2\times \dfrac{1}{60}\times 10\times \dfrac{1}{1000}\) Hint: Include units and make sure answer is in kilometers. |
Question 16 |
Taxicab fares in Boston (Spring 2012) are $2.60 for the first \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile or less and $0.40 for each \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile after that.
Let d represent the distance a passenger travels in miles (with \(d>\dfrac{1}{7}\)). Which of the following expressions represents the total fare?
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40d\) Hint: It's 40 cents for 1/7 of a mile, not per mile. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40\dfrac{d}{7}\) Hint: According to this equation, going 7 miles would cost $3; does that make sense? | |
\( \large \$2.20+\$2.80d\) Hint: You can think of the fare as $2.20 to enter the cab, and then $0.40 for each 1/7 of a mile, including the first 1/7 of a mile (or $2.80 per mile).
Alternatively, you pay $2.60 for the first 1/7 of a mile, and then $2.80 per mile for d-1/7 miles. The total is 2.60+2.80(d-1/7) = 2.60+ 2.80d -.40 = 2.20+2.80d. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$2.80d\) Hint: Don't count the first 1/7 of a mile twice. |
Question 17 |
| I. \(\large \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}\) | II. \( \large .400000\) | III. \(\large\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}\) |
| IV. \( \large 40\% \) | V. \( \large 0.25 \) | VI. \(\large\dfrac{14}{35}\) |
Which of the lists below includes all of the above expressions that are equivalent to \( \dfrac{2}{5}\)?
I, III, V, VIHint: I and V are not at all how fractions and decimals work. | |
III, VIHint: These are right, but there are more. | |
II, III, VIHint: These are right, but there are more. | |
II, III, IV, VI |
Question 18 |
Which property is not shared by all rhombi?
4 congruent sidesHint: The most common definition of a rhombus is a quadrilateral with 4 congruent sides. | |
A center of rotational symmetryHint: The diagonal of a rhombus separates it into two congruent isosceles triangles. The center of this line is a center of 180 degree rotational symmetry that switches the triangles. | |
4 congruent anglesHint: Unless the rhombus is a square, it does not have 4 congruent angles. | |
2 sets of parallel sidesHint: All rhombi are parallelograms. |
Question 19 |
What is the least common multiple of 540 and 216?
\( \large{{2}^{5}}\cdot {{3}^{6}}\cdot 5\) Hint: This is the product of the numbers, not the LCM. | |
\( \large{{2}^{3}}\cdot {{3}^{3}}\cdot 5\) Hint: One way to solve this is to factor both numbers: \(540=2^2 \cdot 3^3 \cdot 5\) and \(216=2^3 \cdot 3^3\). Then for each prime that's a factor of either number, use the largest exponent that appears in one of the factorizations. You can also take the product of the two numbers divided by their GCD. | |
\( \large{{2}^{2}}\cdot {{3}^{3}}\cdot 5\) Hint: 216 is a multiple of 8. | |
\( \large{{2}^{2}}\cdot {{3}^{2}}\cdot {{5}^{2}}\) Hint: Not a multiple of 216 and not a multiple of 540. |
Question 20 |
In each expression below N represents a negative integer. Which expression could have a negative value?
\( \large {{N}^{2}}\) Hint: Squaring always gives a non-negative value. | |
\( \large 6-N\) Hint: A story problem for this expression is, if it was 6 degrees out at noon and N degrees out at sunrise, by how many degrees did the temperature rise by noon? Since N is negative, the answer to this question has to be positive, and more than 6. | |
\( \large -N\) Hint: If N is negative, then -N is positive | |
\( \large 6+N\) Hint: For example, if \(N=-10\), then \(6+N = -4\) |
|
List |
If you found a mistake or have comments on a particular question, please contact me (please copy and paste at least part of the question into the form, as the numbers change depending on how quizzes are displayed). General comments can be left here.
