Hints will display for most wrong answers; explanations for most right answers. You can attempt a question multiple times; it will only be scored correct if you get it right the first time. To see ten new questions, reload the page.
I used the official objectives and sample test to construct these questions, but cannot promise that they accurately reflect what’s on the real test. Some of the sample questions were more convoluted than I could bear to write. See terms of use. See the MTEL Practice Test main page to view questions on a particular topic or to download paper practice tests.
MTEL General Curriculum Mathematics Practice
Question 1 |
A biology class requires a lab fee, which is a whole number of dollars, and the same amount for all students. On Monday the instructor collected $70 in fees, on Tuesday she collected $126, and on Wednesday she collected $266. What is the largest possible amount the fee could be?
$2Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$7Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$14Hint: This is the greatest common factor of 70, 126, and 266. | |
$70Hint: Not a factor of 126 or 266, so couldn't be correct. |
Question 2 |
Use the expression below to answer the question that follows.
\( \large \dfrac{\left( 4\times {{10}^{3}} \right)\times \left( 3\times {{10}^{4}} \right)}{6\times {{10}^{6}}}\)
Which of the following is equivalent to the expression above?
2Hint: \(10^3 \times 10^4=10^7\), and note that if you're guessing when the answers are so closely related, you're generally better off guessing one of the middle numbers. | |
20Hint: \( \dfrac{\left( 4\times {{10}^{3}} \right)\times \left( 3\times {{10}^{4}} \right)}{6\times {{10}^{6}}}=\dfrac {12 \times {{10}^{7}}}{6\times {{10}^{6}}}=\)\(2 \times {{10}^{1}}=20 \) | |
200Hint: \(10^3 \times 10^4=10^7\) | |
2000Hint: \(10^3 \times 10^4=10^7\), and note that if you're guessing when the answers are so closely related, you're generally better off guessing one of the middle numbers. |
Question 3 |
Kendra is trying to decide which fraction is greater, \( \dfrac{4}{7}\) or \( \dfrac{5}{8}\). Which of the following answers shows the best reasoning?
\( \dfrac{4}{7}\) is \( \dfrac{3}{7}\)away from 1, and \( \dfrac{5}{8}\) is \( \dfrac{3}{8}\)away from 1. Since eighth‘s are smaller than seventh‘s, \( \dfrac{5}{8}\) is closer to 1, and is the greater of the two fractions. | |
\( 7-4=3\) and \( 8-5=3\), so the fractions are equal.Hint: Not how to compare fractions. By this logic, 1/2 and 3/4 are equal, but 1/2 and 2/4 are not. | |
\( 4\times 8=32\) and \( 7\times 5=35\). Since \( 32<35\) , \( \dfrac{5}{8}<\dfrac{4}{7}\)Hint: Starts out as something that works, but the conclusion is wrong. 4/7 = 32/56 and 5/8 = 35/56. The cross multiplication gives the numerators, and 35/56 is bigger. | |
\( 4<5\) and \( 7<8\), so \( \dfrac{4}{7}<\dfrac{5}{8}\)Hint: Conclusion is correct, logic is wrong. With this reasoning, 1/2 would be less than 2/100,000. |
Question 4 |
Which property is not shared by all rhombi?
4 congruent sidesHint: The most common definition of a rhombus is a quadrilateral with 4 congruent sides. | |
A center of rotational symmetryHint: The diagonal of a rhombus separates it into two congruent isosceles triangles. The center of this line is a center of 180 degree rotational symmetry that switches the triangles. | |
4 congruent anglesHint: Unless the rhombus is a square, it does not have 4 congruent angles. | |
2 sets of parallel sidesHint: All rhombi are parallelograms. |
Question 5 |
Given that 10 cm is approximately equal to 4 inches, which of the following expressions models a way to find out approximately how many inches are equivalent to 350 cm?
\( \large 350\times \left( \dfrac{10}{4} \right)\) Hint: The final result should be smaller than 350, and this answer is bigger. | |
\( \large 350\times \left( \dfrac{4}{10} \right)\) Hint: Dimensional analysis can help here: \(350 \text{cm} \times \dfrac{4 \text{in}}{10 \text{cm}}\). The cm's cancel and the answer is in inches. | |
\( \large (10-4) \times 350
\) Hint: This answer doesn't make much sense. Try with a simpler example (e.g. 20 cm not 350 cm) to make sure that your logic makes sense. | |
\( \large (350-10) \times 4\) Hint: This answer doesn't make much sense. Try with a simpler example (e.g. 20 cm not 350 cm) to make sure that your logic makes sense. |
Question 6 |
Which of the numbers below is a fraction equivalent to \( 0.\bar{6}\)?
\( \large \dfrac{4}{6}\) Hint: \( 0.\bar{6}=\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{4}{6}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{5}\) Hint: This is equal to 0.6, without the repeating decimal. Answer is equivalent to choice c, which is another way to tell that it's wrong. | |
\( \large \dfrac{6}{10}\) Hint: This is equal to 0.6, without the repeating decimal. Answer is equivalent to choice b, which is another way to tell that it's wrong. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{6}\) Hint: This is less than a half, and \( 0.\bar{6}\) is greater than a half. |
Question 7 |
If two fair coins are flipped, what is the probability that one will come up heads and the other tails?
\( \large \dfrac{1}{4}\) Hint: Think of the coins as a penny and a dime, and list all possibilities. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{3} \) Hint: This is a very common misconception. There are three possible outcomes -- both heads, both tails, and one of each -- but they are not equally likely. Think of the coins as a penny and a dime, and list all possibilities. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2}\) Hint: The possibilities are HH, HT, TH, TT, and all are equally likely. Two of the four have one of each coin, so the probability is 2/4=1/2. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{4}\) Hint: Think of the coins as a penny and a dime, and list all possibilities. |
Question 8 |
Which of the following sets of polygons can be assembled to form a pentagonal pyramid?
2 pentagons and 5 rectangles.Hint: These can be assembled to form a pentagonal prism, not a pentagonal pyramid. | |
1 square and 5 equilateral triangles.Hint: You need a pentagon for a pentagonal pyramid. | |
1 pentagon and 5 isosceles triangles. | |
1 pentagon and 10 isosceles triangles. |
Question 9 |
Use the table below to answer the question that follows:
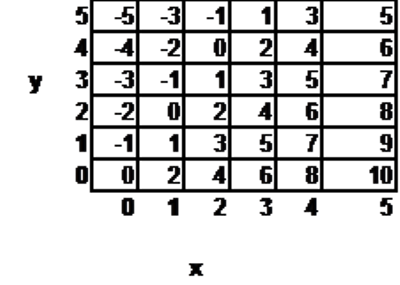
Each number in the table above represents a value W that is determined by the values of x and y. For example, when x=3 and y=1, W=5. What is the value of W when x=9 and y=14? Assume that the patterns in the table continue as shown.
\( \large W=-5\) Hint: When y is even, W is even. | |
\( \large W=4\) Hint: Note that when x increases by 1, W increases by 2, and when y increases by 1, W decreases by 1. At x=y=0, W=0, so at x=9, y=14, W has increased by \(9 \times 2\) and decreased by 14, or W=18-14=4. | |
\( \large W=6\) Hint: Try fixing x or y at 0, and start by finding W for x=0 y=14 or x=9, y=0. | |
\( \large W=32\) Hint: Try fixing x or y at 0, and start by finding W for x=0 y=14 or x=9, y=0. |
Question 10 |
In which table below is y a function of x?
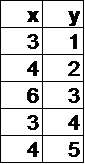 Hint: If x=3, y can have two different values, so it's not a function. | |
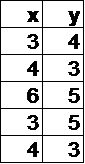 Hint: If x=3, y can have two different values, so it's not a function. | |
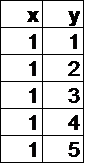 Hint: If x=1, y can have different values, so it's not a function. | |
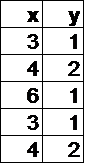 Hint: Each value of x always corresponds to the same value of y. |
If you found a mistake or have comments on a particular question, please contact me (please copy and paste at least part of the question into the form, as the numbers change depending on how quizzes are displayed). General comments can be left here.