Hints will display for most wrong answers; explanations for most right answers. You can attempt a question multiple times; it will only be scored correct if you get it right the first time.
I used the official objectives and sample test to construct these questions, but cannot promise that they accurately reflect what’s on the real test. Some of the sample questions were more convoluted than I could bear to write. See terms of use. See the MTEL Practice Test main page to view questions on a particular topic or to download paper practice tests.
MTEL General Curriculum Mathematics Practice
Question 1 |
A family on vacation drove the first 200 miles in 4 hours and the second 200 miles in 5 hours. Which expression below gives their average speed for the entire trip?
\( \large \dfrac{200+200}{4+5}\) Hint: Average speed is total distance divided by total time. | |
\( \large \left( \dfrac{200}{4}+\dfrac{200}{5} \right)\div 2\) Hint: This seems logical, but the problem is that it weights the first 4 hours and the second 5 hours equally, when each hour should get the same weight in computing the average speed. | |
\( \large \dfrac{200}{4}+\dfrac{200}{5} \) Hint: This would be an average of 90 miles per hour! | |
\( \large \dfrac{400}{4}+\dfrac{400}{5} \) Hint: This would be an average of 180 miles per hour! Even a family of race car drivers probably doesn't have that average speed on a vacation! |
Question 2 |
Use the problem below to answer the question that follows:
T shirts are on sale for 20% off. Tasha paid $8.73 for a shirt. What is the regular price of the shirt? There is no tax on clothing purchases under $175.
Let p represent the regular price of these t-shirt. Which of the following equations is correct?
\( \large 0.8p=\$8.73\) Hint: 80% of the regular price = $8.73. | |
\( \large \$8.73+0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice c. | |
\( \large 1.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice b. | |
\( \large p-0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: Subtract p from both sides of this equation, and you have -.2 x 8.73 =0. |
Question 3 |
The "houses" below are made of toothpicks and gum drops.
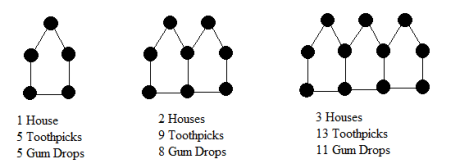
How many toothpicks are there in a row of 53 houses?
212Hint: Can the number of toothpicks be even? | |
213Hint: One way to see this is that every new "house" adds 4 toothpicks to the leftmost vertical toothpick -- so the total number is 1 plus 4 times the number of "houses." There are many other ways to look at the problem too. | |
217Hint: Try your strategy with a smaller number of "houses" so you can count and find your mistake. | |
265Hint: Remember that the "houses" overlap some walls. |
Question 4 |
Which of the following inequalities describes all values of x with \(\large \dfrac{x}{2}\le \dfrac{x}{3}\)?
\( \large x < 0\) Hint: If x =0, then x/2 = x/3, so this answer can't be correct. | |
\( \large x \le 0\) | |
\( \large x > 0\) Hint: If x =0, then x/2 = x/3, so this answer can't be correct. | |
\( \large x \ge 0\) Hint: Try plugging in x = 6. |
Question 5 |
The expression \( \large {{7}^{-4}}\cdot {{8}^{-6}}\) is equal to which of the following?
\( \large \dfrac{8}{{{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) Hint: The bases are whole numbers, and the exponents are negative. How can the numerator be 8? | |
\( \large \dfrac{64}{{{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) Hint: The bases are whole numbers, and the exponents are negative. How can the numerator be 64? | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{8\cdot {{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) Hint: \(8^{-6}=8^{-4} \times 8^{-2}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{64\cdot {{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) |
Question 6 |
Which of the lists below is in order from least to greatest value?
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2},\quad \dfrac{1}{3},\quad \dfrac{1}{4},\quad \dfrac{1}{5}\) Hint: This is ordered from greatest to least. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{3},\quad \dfrac{2}{7},\quad \dfrac{3}{8},\quad \dfrac{4}{11}\) Hint: 1/3 = 2/6 is bigger than 2/7. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{4},\quad \dfrac{2}{5},\quad \dfrac{2}{3},\quad \dfrac{4}{5}\) Hint: One way to look at this: 1/4 and 2/5 are both less than 1/2, and 2/3 and 4/5 are both greater than 1/2. 1/4 is 25% and 2/5 is 40%, so 2/5 is greater. The distance from 2/3 to 1 is 1/3 and from 4/5 to 1 is 1/5, and 1/5 is less than 1/3, so 4/5 is bigger. | |
\( \large \dfrac{7}{8},\quad \dfrac{6}{7},\quad \dfrac{5}{6},\quad \dfrac{4}{5}\) Hint: This is in order from greatest to least. |
Question 7 |
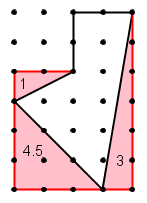
The picture below represents a board with pegs on it, where the closest distance between two pegs is 1 cm. What is the area of the pentagon shown?
Question 8 |
Solve for x: \(\large 4-\dfrac{2}{3}x=2x\)
\( \large x=3\) Hint: Try plugging x=3 into the equation. | |
\( \large x=-3\) Hint: Left side is positive, right side is negative when you plug this in for x. | |
\( \large x=\dfrac{3}{2}\) Hint: One way to solve: \(4=\dfrac{2}{3}x+2x\) \(=\dfrac{8}{3}x\).\(x=\dfrac{3 \times 4}{8}=\dfrac{3}{2}\). Another way is to just plug x=3/2 into the equation and see that each side equals 3 -- on a multiple choice test, you almost never have to actually solve for x. | |
\( \large x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\) Hint: Left side is positive, right side is negative when you plug this in for x. |
Question 9 |
The expression \( \large{{8}^{3}}\cdot {{2}^{-10}}\) is equal to which of the following?
\( \large 2\) Hint: Write \(8^3\) as a power of 2. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2}\) Hint: \(8^3 \cdot {2}^{-10}={(2^3)}^3 \cdot {2}^{-10}\) =\(2^9 \cdot {2}^{-10} =2^{-1}\) | |
\( \large 16\) Hint: Write \(8^3\) as a power of 2. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{16}\) Hint: Write \(8^3\) as a power of 2. |
Question 10 |
Taxicab fares in Boston (Spring 2012) are $2.60 for the first \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile or less and $0.40 for each \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile after that.
Let d represent the distance a passenger travels in miles (with \(d>\dfrac{1}{7}\)). Which of the following expressions represents the total fare?
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40d\) Hint: It's 40 cents for 1/7 of a mile, not per mile. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40\dfrac{d}{7}\) Hint: According to this equation, going 7 miles would cost $3; does that make sense? | |
\( \large \$2.20+\$2.80d\) Hint: You can think of the fare as $2.20 to enter the cab, and then $0.40 for each 1/7 of a mile, including the first 1/7 of a mile (or $2.80 per mile).
Alternatively, you pay $2.60 for the first 1/7 of a mile, and then $2.80 per mile for d-1/7 miles. The total is 2.60+2.80(d-1/7) = 2.60+ 2.80d -.40 = 2.20+2.80d. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$2.80d\) Hint: Don't count the first 1/7 of a mile twice. |
Question 11 |
The pattern below consists of a row of black squares surrounded by white squares.
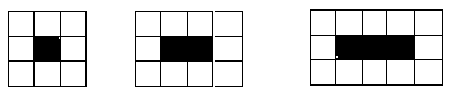
How many white squares would surround a row of 157 black squares?
314Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. | |
317Hint: Are there ever an odd number of white squares? | |
320Hint: One way to see this is that there are 6 tiles on the left and right ends, and the rest of the white tiles are twice the number of black tiles (there are many other ways to look at it too). | |
322Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. |
Question 12 |
What is the length of side \(\overline{BD}\) in the triangle below, where \(\angle DBA\) is a right angle?
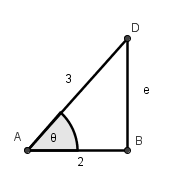
\( \large 1\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem. | |
\( \large \sqrt{5}\) Hint: \(2^2+e^2=3^2\) or \(4+e^2=9;e^2=5; e=\sqrt{5}\). | |
\( \large \sqrt{13}\) Hint: e is not the hypotenuse. | |
\( \large 5\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem. |
Question 13 |
A family has four children. What is the probability that two children are girls and two are boys? Assume the the probability of having a boy (or a girl) is 50%.
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2}\) Hint: How many different configurations are there from oldest to youngest, e.g. BGGG? How many of them have 2 boys and 2 girls? | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{4}\) Hint: How many different configurations are there from oldest to youngest, e.g. BGGG? How many of them have 2 boys and 2 girls? | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{5}\) Hint: Some configurations are more probable than others -- i.e. it's more likely to have two boys and two girls than all boys. Be sure you are weighting properly. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{8}\) Hint: There are two possibilities for each child, so there are \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 =16\) different configurations, e.g. from oldest to youngest BBBG, BGGB, GBBB, etc. Of these configurations, there are 6 with two boys and two girls (this is the combination \(_{4}C_{2}\) or "4 choose 2"): BBGG, BGBG, BGGB, GGBB, GBGB, and GBBG. Thus the probability is 6/16=3/8. |
Question 14 |
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows:
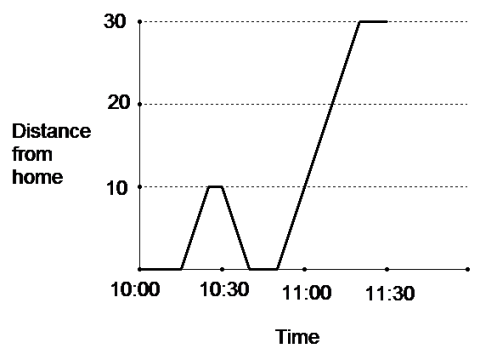
The graph above best matches which of the following scenarios:
George left home at 10:00 and drove to work on a crooked path. He was stopped in traffic at 10:30 and 10:45. He drove 30 miles total.Hint: Just because he ended up 30 miles from home doesn't mean he drove 30 miles total. | |
George drove to work. On the way to work there is a little hill and a big hill. He slowed down for them. He made it to work at 11:15.Hint: The graph is not a picture of the roads. | |
George left home at 10:15. He drove 10 miles, then realized he‘d forgotten something at home. He turned back and got what he‘d forgotten. Then he drove in a straight line, at many different speeds, until he got to work around 11:15.Hint: A straight line on a distance versus time graph means constant speed. | |
George left home at 10:15. He drove 10 miles, then realized he‘d forgotten something at home. He turned back and got what he‘d forgotten. Then he drove at a constant speed until he got to work around 11:15. |
Question 15 |
Which of the following is equivalent to \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}?\)
\( \large \dfrac{7}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2}\) Hint: Addition and subtraction are of equal priority in the order of operations -- do them left to right. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{4}\) Hint: \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}+-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. |
Question 16 |
Which of the lines depicted below is a graph of \( \large y=2x-5\)?
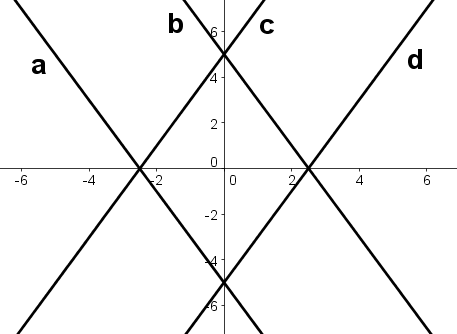
aHint: The slope of line a is negative. | |
bHint: Wrong slope and wrong intercept. | |
cHint: The intercept of line c is positive. | |
dHint: Slope is 2 -- for every increase of 1 in x, y increases by 2. Intercept is -5 -- the point (0,-5) is on the line. |
Question 17 |
There are 15 students for every teacher. Let t represent the number of teachers and let s represent the number of students. Which of the following equations is correct?
\( \large t=s+15\) Hint: When there are 2 teachers, how many students should there be? Do those values satisfy this equation? | |
\( \large s=t+15\) Hint: When there are 2 teachers, how many students should there be? Do those values satisfy this equation? | |
\( \large t=15s\) Hint: This is a really easy mistake to make, which comes from transcribing directly from English, "1 teachers equals 15 students." To see that it's wrong, plug in s=2; do you really need 30 teachers for 2 students? To avoid this mistake, insert the word "number," "Number of teachers equals 15 times number of students" is more clearly problematic. | |
\( \large s=15t\) |
Question 18 |
Use the expression below to answer the question that follows.
\( \large 3\times {{10}^{4}}+2.2\times {{10}^{2}}\)
Which of the following is closest to the expression above?
Five millionHint: Pay attention to the exponents. Adding 3 and 2 doesn't work because they have different place values. | |
Fifty thousandHint: Pay attention to the exponents. Adding 3 and 2 doesn't work because they have different place values. | |
Three millionHint: Don't add the exponents. | |
Thirty thousandHint: \( 3\times {{10}^{4}} = 30,000;\) the other term is much smaller and doesn't change the estimate. |
Question 19 |
The letters A, and B represent digits (possibly equal) in the ten digit number x=1,438,152,A3B. For which values of A and B is x divisible by 12, but not by 9?
\( \large A = 0, B = 4\) Hint: Digits add to 31, so not divisible by 3, so not divisible by 12. | |
\( \large A = 7, B = 2\) Hint: Digits add to 36, so divisible by 9. | |
\( \large A = 0, B = 6\) Hint: Digits add to 33, divisible by 3, not 9. Last digits are 36, so divisible by 4, and hence by 12. | |
\( \large A = 4, B = 8\) Hint: Digits add to 39, divisible by 3, not 9. Last digits are 38, so not divisible by 4, so not divisible by 12. |
Question 20 |
The window glass below has the shape of a semi-circle on top of a square, where the side of the square has length x. It was cut from one piece of glass.
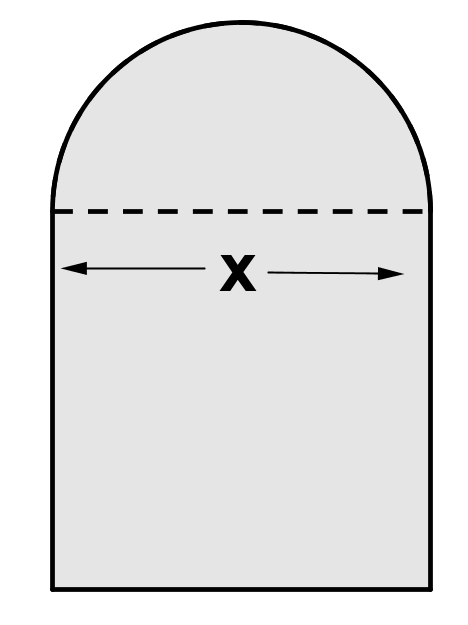
What is the perimeter of the window glass?
\( \large 3x+\dfrac{\pi x}{2}\) Hint: By definition, \(\pi\) is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter; thus the circumference is \(\pi d\). Since we have a semi-circle, its perimeter is \( \dfrac{1}{2} \pi x\). Only 3 sides of the square contribute to the perimeter. | |
\( \large 3x+2\pi x\) Hint: Make sure you know how to find the circumference of a circle. | |
\( \large 3x+\pi x\) Hint: Remember it's a semi-circle, not a circle. | |
\( \large 4x+2\pi x\) Hint: Only 3 sides of the square contribute to the perimeter. |
|
List |
If you found a mistake or have comments on a particular question, please contact me (please copy and paste at least part of the question into the form, as the numbers change depending on how quizzes are displayed). General comments can be left here.