Hints will display for most wrong answers; explanations for most right answers. You can attempt a question multiple times; it will only be scored correct if you get it right the first time.
I used the official objectives and sample test to construct these questions, but cannot promise that they accurately reflect what’s on the real test. Some of the sample questions were more convoluted than I could bear to write. See terms of use. See the MTEL Practice Test main page to view questions on a particular topic or to download paper practice tests.
MTEL General Curriculum Mathematics Practice
Question 1 |
A homeowner is planning to tile the kitchen floor with tiles that measure 6 inches by 8 inches. The kitchen floor is a rectangle that measures 10 ft by 12 ft, and there are no gaps between the tiles. How many tiles does the homeowner need?
30Hint: The floor is 120 sq feet, and the tiles are smaller than 1 sq foot. Also, remember that 1 sq foot is 12 \(\times\) 12=144 sq inches. | |
120Hint: The floor is 120 sq feet, and the tiles are smaller than 1 sq foot. | |
300Hint: Recheck your calculations. | |
360Hint: One way to do this is to note that 6 inches = 1/2 foot and 8 inches = 2/3 foot, so the area of each tile is 1/2 \(\times\) 2/3=1/3 sq foot, or each square foot of floor requires 3 tiles. The area of the floor is 120 square feet. Note that the tiles would fit evenly oriented in either direction, parallel to the walls. |
Question 2 |
An above-ground swimming pool is in the shape of a regular hexagonal prism, is one meter high, and holds 65 cubic meters of water. A second pool has a base that is also a regular hexagon, but with sides twice as long as the sides in the first pool. This second pool is also one meter high. How much water will the second pool hold?
\( \large 65\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}\) Hint: A bigger pool would hold more water. | |
\( \large 65\cdot 2\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}\) Hint: Try a simpler example, say doubling the sides of the base of a 1 x 1 x 1 cube. | |
\( \large 65\cdot 4\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}\) Hint: If we think of the pool as filled with 1 x 1 x 1 cubes (and some fractions of cubes), then scaling to the larger pool changes each 1 x 1 x 1 cube to a 2 x 2 x 1 prism, or multiplies volume by 4. | |
\( \large 65\cdot 8\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}\) Hint: Try a simpler example, say doubling the sides of the base of a 1 x 1 x 1 cube. |
Question 3 |
Use the expression below to answer the question that follows.
\( \large 3\times {{10}^{4}}+2.2\times {{10}^{2}}\)
Which of the following is closest to the expression above?
Five millionHint: Pay attention to the exponents. Adding 3 and 2 doesn't work because they have different place values. | |
Fifty thousandHint: Pay attention to the exponents. Adding 3 and 2 doesn't work because they have different place values. | |
Three millionHint: Don't add the exponents. | |
Thirty thousandHint: \( 3\times {{10}^{4}} = 30,000;\) the other term is much smaller and doesn't change the estimate. |
Question 4 |
Kendra is trying to decide which fraction is greater, \( \dfrac{4}{7}\) or \( \dfrac{5}{8}\). Which of the following answers shows the best reasoning?
\( \dfrac{4}{7}\) is \( \dfrac{3}{7}\)away from 1, and \( \dfrac{5}{8}\) is \( \dfrac{3}{8}\)away from 1. Since eighth‘s are smaller than seventh‘s, \( \dfrac{5}{8}\) is closer to 1, and is the greater of the two fractions. | |
\( 7-4=3\) and \( 8-5=3\), so the fractions are equal.Hint: Not how to compare fractions. By this logic, 1/2 and 3/4 are equal, but 1/2 and 2/4 are not. | |
\( 4\times 8=32\) and \( 7\times 5=35\). Since \( 32<35\) , \( \dfrac{5}{8}<\dfrac{4}{7}\)Hint: Starts out as something that works, but the conclusion is wrong. 4/7 = 32/56 and 5/8 = 35/56. The cross multiplication gives the numerators, and 35/56 is bigger. | |
\( 4<5\) and \( 7<8\), so \( \dfrac{4}{7}<\dfrac{5}{8}\)Hint: Conclusion is correct, logic is wrong. With this reasoning, 1/2 would be less than 2/100,000. |
Question 5 |
The polygon depicted below is drawn on dot paper, with the dots spaced 1 unit apart. What is the perimeter of the polygon?

\( \large 18+\sqrt{2} \text{ units}\) Hint: Be careful with the Pythagorean Theorem. | |
\( \large 18+2\sqrt{2}\text{ units}\) Hint: There are 13 horizontal or vertical 1 unit segments. The longer diagonal is the hypotenuse of a 3-4-5 right triangle, so its length is 5 units. The shorter diagonal is the hypotenuse of a 45-45-90 right triangle with side 2, so its hypotenuse has length \(2 \sqrt{2}\). | |
\( \large 18 \text{ units}
\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the diagonal segments. | |
\( \large 20 \text{ units}\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the diagonal segments. |
Question 6 |
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows:
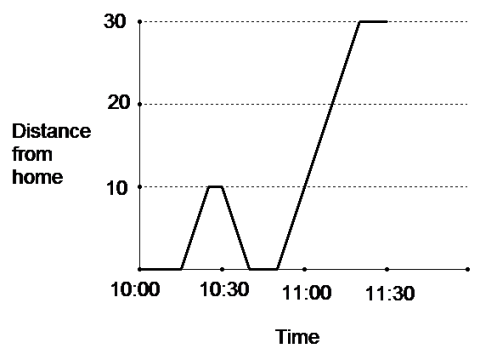
The graph above best matches which of the following scenarios:
George left home at 10:00 and drove to work on a crooked path. He was stopped in traffic at 10:30 and 10:45. He drove 30 miles total.Hint: Just because he ended up 30 miles from home doesn't mean he drove 30 miles total. | |
George drove to work. On the way to work there is a little hill and a big hill. He slowed down for them. He made it to work at 11:15.Hint: The graph is not a picture of the roads. | |
George left home at 10:15. He drove 10 miles, then realized he‘d forgotten something at home. He turned back and got what he‘d forgotten. Then he drove in a straight line, at many different speeds, until he got to work around 11:15.Hint: A straight line on a distance versus time graph means constant speed. | |
George left home at 10:15. He drove 10 miles, then realized he‘d forgotten something at home. He turned back and got what he‘d forgotten. Then he drove at a constant speed until he got to work around 11:15. |
Question 7 |
Use the four figures below to answer the question that follows:

How many of the figures pictured above have at least one line of reflective symmetry?
\( \large 1\) | |
\( \large 2\) Hint: The ellipse has 2 lines of reflective symmetry (horizontal and vertical, through the center) and the triangle has 3. The other two figures have rotational symmetry, but not reflective symmetry. | |
\( \large 3\) | |
\( \large 4\) Hint: All four have rotational symmetry, but not reflective symmetry. |
Question 8 |
The speed of sound in dry air at 68 degrees F is 343.2 meters per second. Which of the expressions below could be used to compute the number of kilometers that a sound wave travels in 10 minutes (in dry air at 68 degrees F)?
\( \large 343.2\times 60\times 10\) Hint: In kilometers, not meters. | |
\( \large 343.2\times 60\times 10\times \dfrac{1}{1000}\) Hint: Units are meters/sec \(\times\) seconds/minute \(\times\) minutes \(\times\) kilometers/meter, and the answer is in kilometers. | |
\( \large 343.2\times \dfrac{1}{60}\times 10\) Hint: Include units and make sure answer is in kilometers. | |
\( \large 343.2\times \dfrac{1}{60}\times 10\times \dfrac{1}{1000}\) Hint: Include units and make sure answer is in kilometers. |
Question 9 |
There are 15 students for every teacher. Let t represent the number of teachers and let s represent the number of students. Which of the following equations is correct?
\( \large t=s+15\) Hint: When there are 2 teachers, how many students should there be? Do those values satisfy this equation? | |
\( \large s=t+15\) Hint: When there are 2 teachers, how many students should there be? Do those values satisfy this equation? | |
\( \large t=15s\) Hint: This is a really easy mistake to make, which comes from transcribing directly from English, "1 teachers equals 15 students." To see that it's wrong, plug in s=2; do you really need 30 teachers for 2 students? To avoid this mistake, insert the word "number," "Number of teachers equals 15 times number of students" is more clearly problematic. | |
\( \large s=15t\) |
Question 10 |
The following story situations model \( 12\div 3\):
I) Jack has 12 cookies, which he wants to share equally between himself and two friends. How many cookies does each person get?
II) Trent has 12 cookies, which he wants to put into bags of 3 cookies each. How many bags can he make?
III) Cicely has $12. Cookies cost $3 each. How many cookies can she buy?
Which of these questions illustrate the same model of division, either partitive (partioning) or measurement (quotative)?
I and II | |
I and III | |
II and IIIHint: Problem I is partitive (or partitioning or sharing) -- we put 12 objects into 3 groups. Problems II and III are quotative (or measurement) -- we put 12 objects in groups of 3. | |
All three problems model the same meaning of division |
Question 11 |
| I. \(\large \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}\) | II. \( \large .400000\) | III. \(\large\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}\) |
| IV. \( \large 40\% \) | V. \( \large 0.25 \) | VI. \(\large\dfrac{14}{35}\) |
Which of the lists below includes all of the above expressions that are equivalent to \( \dfrac{2}{5}\)?
I, III, V, VIHint: I and V are not at all how fractions and decimals work. | |
III, VIHint: These are right, but there are more. | |
II, III, VIHint: These are right, but there are more. | |
II, III, IV, VI |
Question 12 |
What is the length of side \(\overline{BD}\) in the triangle below, where \(\angle DBA\) is a right angle?
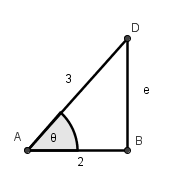
\( \large 1\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem. | |
\( \large \sqrt{5}\) Hint: \(2^2+e^2=3^2\) or \(4+e^2=9;e^2=5; e=\sqrt{5}\). | |
\( \large \sqrt{13}\) Hint: e is not the hypotenuse. | |
\( \large 5\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem. |
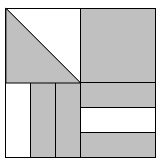
Question 13 |
\( \large \dfrac{17}{24}\) Hint: You might try adding segments so each quadrant is divided into 6 pieces with equal area -- there will be 24 regions, not all the same shape, but all the same area, with 17 of them shaded (for the top left quarter, you could also first change the diagonal line to a horizontal or vertical line that divides the square in two equal pieces and shade one) . | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{4}\) Hint: Be sure you're taking into account the different sizes of the pieces. | |
\( \large \dfrac{2}{3}\) Hint: The bottom half of the picture is 2/3 shaded, and the top half is more than 2/3 shaded, so this answer is too small. | |
\( \large \dfrac{17}{6} \) Hint: This answer is bigger than 1, so doesn't make any sense. Be sure you are using the whole picture, not one quadrant, as the unit. |
Question 14 |
Which of the graphs below represent functions?
I.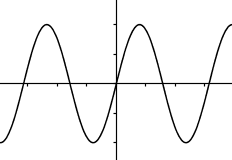 II.
II. 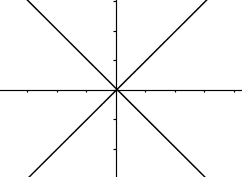 III.
III. 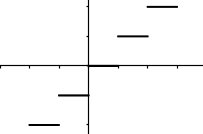 IV.
IV. 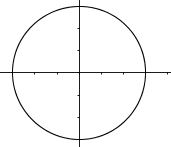
I and IV only.Hint: There are vertical lines that go through 2 points in IV . | |
I and III only.Hint: Even though III is not continuous, it's still a function (assuming that vertical lines between the "steps" do not go through 2 points). | |
II and III only.Hint: Learn about the vertical line test. | |
I, II, and IV only.Hint: There are vertical lines that go through 2 points in II. |
Question 15 |
The "houses" below are made of toothpicks and gum drops.
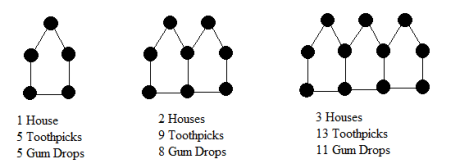
How many toothpicks are there in a row of 53 houses?
212Hint: Can the number of toothpicks be even? | |
213Hint: One way to see this is that every new "house" adds 4 toothpicks to the leftmost vertical toothpick -- so the total number is 1 plus 4 times the number of "houses." There are many other ways to look at the problem too. | |
217Hint: Try your strategy with a smaller number of "houses" so you can count and find your mistake. | |
265Hint: Remember that the "houses" overlap some walls. |
Question 16 |
A car is traveling at 60 miles per hour. Which of the expressions below could be used to compute how many feet the car travels in 1 second? Note that 1 mile = 5,280 feet.
\( \large 60\dfrac{\text{miles}}{\text{hour}}\cdot 5280\dfrac{\text{feet}}{\text{mile}}\cdot 60\dfrac{\text{minutes}}{\text{hour}}\cdot 60\dfrac{\text{seconds}}{\text{minute}}
\) Hint: This answer is not in feet/second. | |
\( \large 60\dfrac{\text{miles}}{\text{hour}}\cdot 5280\dfrac{\text{feet}}{\text{mile}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{60}\dfrac{\text{hour}}{\text{minutes}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{60}\dfrac{\text{minute}}{\text{seconds}}
\) Hint: This is the only choice where the answer is in feet per second and the unit conversions are correct. | |
\( \large 60\dfrac{\text{miles}}{\text{hour}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{5280}\dfrac{\text{foot}}{\text{miles}}\cdot 60\dfrac{\text{hours}}{\text{minute}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{60}\dfrac{\text{minute}}{\text{seconds}}\) Hint: Are there really 60 hours in a minute? | |
\( \large 60\dfrac{\text{miles}}{\text{hour}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{5280}\dfrac{\text{mile}}{\text{feet}}\cdot 60\dfrac{\text{minutes}}{\text{hour}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{60}\dfrac{\text{minute}}{\text{seconds}}\) Hint: This answer is not in feet/second. |
Question 17 |
The histogram below shows the frequency of a class's scores on a 4 question quiz.
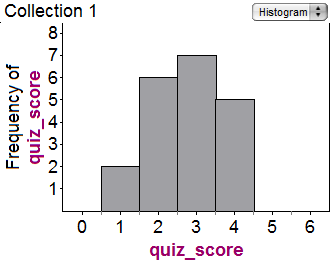
What was the mean score on the quiz?
\( \large 2.75\) Hint: There were 20 students who took the quiz. Total points earned: \(2 \times 1+6 \times 2+ 7\times 3+5 \times 4=55\), and 55/20 = 2.75. | |
\( \large 2\) Hint: How many students are there total? Did you count them all? | |
\( \large 3\) Hint: How many students are there total? Did you count them all? Be sure you're finding the mean, not the median or the mode. | |
\( \large 2.5\) Hint: How many students are there total? Did you count them all? Don't just take the mean of 1, 2, 3, 4 -- you have to weight them properly. |
Question 18 |
Which of the lines depicted below is a graph of \( \large y=2x-5\)?
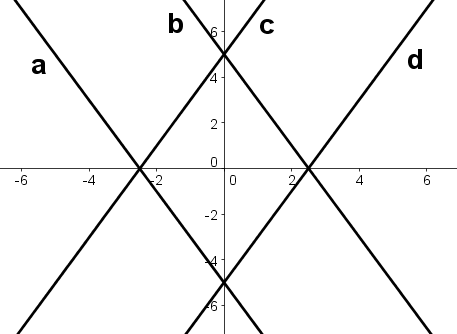
aHint: The slope of line a is negative. | |
bHint: Wrong slope and wrong intercept. | |
cHint: The intercept of line c is positive. | |
dHint: Slope is 2 -- for every increase of 1 in x, y increases by 2. Intercept is -5 -- the point (0,-5) is on the line. |
Question 19 |
A teacher has a list of all the countries in the world and their populations in March 2012. She is going to have her students use technology to compute the mean and median of the numbers on the list. Which of the following statements is true?
The teacher can be sure that the mean and median will be the same without doing any computation.Hint: Does this make sense? How likely is it that the mean and median of any large data set will be the same? | |
The teacher can be sure that the mean is bigger than the median without doing any computation.Hint: This is a skewed distribution, and very large countries like China and India contribute huge numbers to the mean, but are counted the same as small countries like Luxembourg in the median (the same thing happens w/data on salaries, where a few very high income people tilt the mean -- that's why such data is usually reported as medians). | |
The teacher can be sure that the median is bigger than the mean without doing any computation.Hint: Think about a set of numbers like 1, 2, 3, 4, 10,000 -- how do the mean/median compare? How might that relate to countries of the world? | |
There is no way for the teacher to know the relative size of the mean and median without computing them.Hint: Knowing the shape of the distribution of populations does give us enough info to know the relative size of the mean and median, even without computing them. |
Question 20 |
Taxicab fares in Boston (Spring 2012) are $2.60 for the first \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile or less and $0.40 for each \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile after that.
Let d represent the distance a passenger travels in miles (with \(d>\dfrac{1}{7}\)). Which of the following expressions represents the total fare?
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40d\) Hint: It's 40 cents for 1/7 of a mile, not per mile. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40\dfrac{d}{7}\) Hint: According to this equation, going 7 miles would cost $3; does that make sense? | |
\( \large \$2.20+\$2.80d\) Hint: You can think of the fare as $2.20 to enter the cab, and then $0.40 for each 1/7 of a mile, including the first 1/7 of a mile (or $2.80 per mile).
Alternatively, you pay $2.60 for the first 1/7 of a mile, and then $2.80 per mile for d-1/7 miles. The total is 2.60+2.80(d-1/7) = 2.60+ 2.80d -.40 = 2.20+2.80d. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$2.80d\) Hint: Don't count the first 1/7 of a mile twice. |
Question 21 |
Use the solution procedure below to answer the question that follows:
\( \large {\left( x+3 \right)}^{2}=10\)
\( \large \left( x+3 \right)\left( x+3 \right)=10\)
\( \large {x}^{2}+9=10\)
\( \large {x}^{2}+9-9=10-9\)
\( \large {x}^{2}=1\)
\( \large x=1\text{ or }x=-1\)
Which of the following is incorrect in the procedure shown above?
The commutative property is used incorrectly.Hint: The commutative property is \(a+b=b+a\) or \(ab=ba\). | |
The associative property is used incorrectly.Hint: The associative property is \(a+(b+c)=(a+b)+c\) or
\(a \times (b \times c)=(a \times b) \times c\). | |
Order of operations is done incorrectly. | |
The distributive property is used incorrectly.Hint: \((x+3)(x+3)=x(x+3)+3(x+3)\)=\(x^2+3x+3x+9.\) |
Question 22 |
The least common multiple of 60 and N is 1260. Which of the following could be the prime factorization of N?
\( \large2\cdot 5\cdot 7\) Hint: 1260 is divisible by 9 and 60 is not, so N must be divisible by 9 for 1260 to be the LCM. | |
\( \large{{2}^{3}}\cdot {{3}^{2}}\cdot 5 \cdot 7\) Hint: 1260 is not divisible by 8, so it isn't a multiple of this N. | |
\( \large3 \cdot 5 \cdot 7\) Hint: 1260 is divisible by 9 and 60 is not, so N must be divisible by 9 for 1260 to be the LCM. | |
\( \large{{3}^{2}}\cdot 5\cdot 7\) Hint: \(1260=2^2 \cdot 3^2 \cdot 5 \cdot 7\) and \(60=2^2 \cdot 3 \cdot 5\). In order for 1260 to be the LCM, N has to be a multiple of \(3^2\) and of 7 (because 60 is not a multiple of either of these). N also cannot introduce a factor that would require the LCM to be larger (as in choice b). |
Question 23 |
Which of the following values of x satisfies the inequality \( \large \left| {{(x+2)}^{3}} \right|<3?\)
\( \large x=-3\) Hint: \( \left| {{(-3+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {(-1)}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | -1 \right |=1 \) . | |
\( \large x=0\) Hint: \( \left| {{(0+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {2}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | 8 \right | \) =\( 8\) | |
\( \large x=-4\) Hint: \( \left| {{(-4+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {(-2)}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | -8 \right | \) =\( 8\) | |
\( \large x=1\) Hint: \( \left| {{(1+2)}^{3}} \right|\)=\( \left | {3}^3 \right | \)=\( \left | 27 \right | \) = \(27\) |
Question 24 |
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
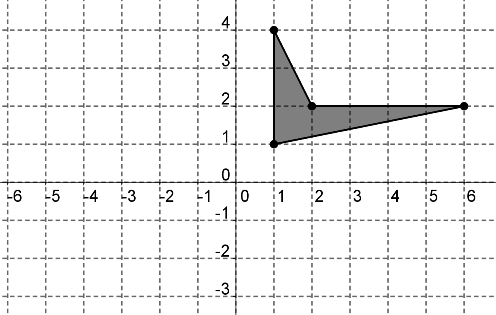
If the polygon shown above is reflected about the y axis and then rotated 90 degrees clockwise about the origin, which of the following graphs is the result?
 Hint: Try following the point (1,4) to see where it goes after each transformation. | |
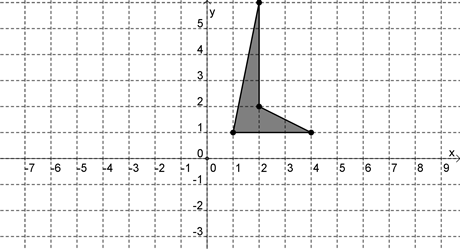 | |
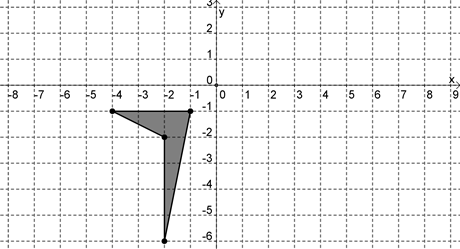
Hint: Make sure you're reflecting in the correct axis. | |
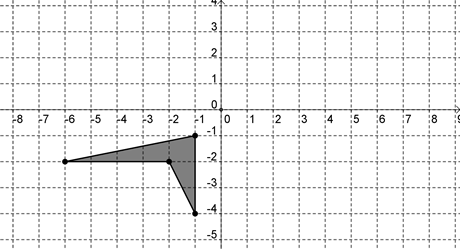 Hint: Make sure you're rotating the correct direction. |
Question 25 |
A solution requires 4 ml of saline for every 7 ml of medicine. How much saline would be required for 50 ml of medicine?
\( \large 28 \dfrac{4}{7}\) ml Hint: 49 ml of medicine requires 28 ml of saline. The extra ml of saline requires 4 ml saline/ 7 ml medicine = 4/7 ml saline per 1 ml medicine. | |
\( \large 28 \dfrac{1}{4}\) ml Hint: 49 ml of medicine requires 28 ml of saline. How much saline does the extra ml require? | |
\( \large 28 \dfrac{1}{7}\) ml Hint: 49 ml of medicine requires 28 ml of saline. How much saline does the extra ml require? | |
\( \large 87.5\) ml Hint: 49 ml of medicine requires 28 ml of saline. How much saline does the extra ml require? |
Question 26 |
Which of the following is equal to eleven billion four hundred thousand?
\( \large 11,400,000\) Hint: That's eleven million four hundred thousand. | |
\(\large11,000,400,000\) | |
\( \large11,000,000,400,000\) Hint: That's eleven trillion four hundred thousand (although with British conventions; this answer is correct, but in the US, it isn't). | |
\( \large 11,400,000,000\) Hint: That's eleven billion four hundred million |
Question 27 |
Which of the following inequalities describes all values of x with \(\large \dfrac{x}{2}\le \dfrac{x}{3}\)?
\( \large x < 0\) Hint: If x =0, then x/2 = x/3, so this answer can't be correct. | |
\( \large x \le 0\) | |
\( \large x > 0\) Hint: If x =0, then x/2 = x/3, so this answer can't be correct. | |
\( \large x \ge 0\) Hint: Try plugging in x = 6. |
Question 28 |
The expression \( \large {{7}^{-4}}\cdot {{8}^{-6}}\) is equal to which of the following?
\( \large \dfrac{8}{{{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) Hint: The bases are whole numbers, and the exponents are negative. How can the numerator be 8? | |
\( \large \dfrac{64}{{{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) Hint: The bases are whole numbers, and the exponents are negative. How can the numerator be 64? | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{8\cdot {{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) Hint: \(8^{-6}=8^{-4} \times 8^{-2}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{64\cdot {{\left( 56 \right)}^{4}}}\) |
Question 29 |
A family went on a long car trip. Below is a graph of how far they had driven at each hour.
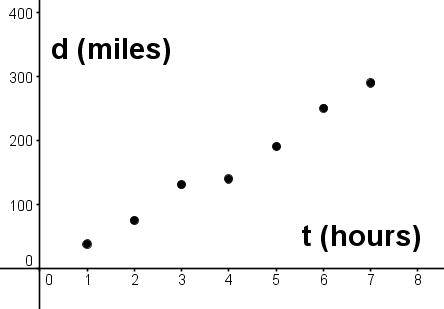
Which of the following is closest to their average speed driving on the trip?
\( \large d=20t\) Hint: Try plugging t=7 into the equation, and see how it matches the graph. | |
\( \large d=30t\) Hint: Try plugging t=7 into the equation, and see how it matches the graph. | |
\( \large d=40t\) | |
\( \large d=50t\) Hint: Try plugging t=7 into the equation, and see how it matches the graph. |
Question 30 |
Here are some statements:
I) 5 is an integer II)\( -5 \) is an integer III) \(0\) is an integer
Which of the statements are true?
I only | |
I and II only | |
I and III only | |
I, II, and IIIHint: The integers are ...-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, .... |
Question 31 |
The table below gives the result of a survey at a college, asking students whether they were residents or commuters:
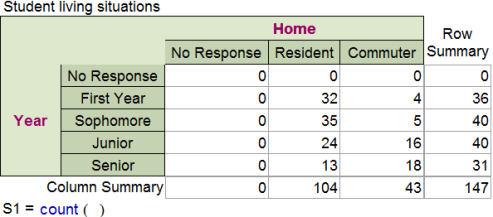
Based on the above data, what is the probability that a randomly chosen commuter student is a junior or a senior?
\( \large \dfrac{34}{43}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{34}{71}\) Hint: This is the probability that a randomly chosen junior or senior is a commuter student. | |
\( \large \dfrac{34}{147}\) Hint: This is the probability that a randomly chosen student is a junior or senior who is a commuter. | |
\( \large \dfrac{71}{147}\) Hint: This is the probability that a randomly chosen student is a junior or a senior. |
Question 32 |
What is the greatest common factor of 540 and 216?
\( \large{{2}^{2}}\cdot {{3}^{3}}\) Hint: One way to solve this is to factor both numbers: \(540=2^2 \cdot 3^3 \cdot 5\) and \(216=2^3 \cdot 3^3\). Then take the smaller power for each prime that is a factor of both numbers. | |
\( \large2\cdot 3\) Hint: This is a common factor of both numbers, but it's not the greatest common factor. | |
\( \large{{2}^{3}}\cdot {{3}^{3}}\) Hint: \(2^3 = 8\) is not a factor of 540. | |
\( \large{{2}^{2}}\cdot {{3}^{2}}\) Hint: This is a common factor of both numbers, but it's not the greatest common factor. |
Question 33 |
Which of the following is equivalent to
\( \large A-B+C\div D\times E\)?
\( \large A-B-\dfrac{C}{DE}
\) Hint: In the order of operations, multiplication and division have the same priority, so do them left to right; same with addition and subtraction. | |
\( \large A-B+\dfrac{CE}{D}\) Hint: In practice, you're better off using parentheses than writing an expression like the one in the question. The PEMDAS acronym that many people memorize is misleading. Multiplication and division have equal priority and are done left to right. They have higher priority than addition and subtraction. Addition and subtraction also have equal priority and are done left to right. | |
\( \large \dfrac{AE-BE+CE}{D}\) Hint: Use order of operations, don't just compute left to right. | |
\( \large A-B+\dfrac{C}{DE}\) Hint: In the order of operations, multiplication and division have the same priority, so do them left to right |
Question 34 |
Use the problem below to answer the question that follows:
T shirts are on sale for 20% off. Tasha paid $8.73 for a shirt. What is the regular price of the shirt? There is no tax on clothing purchases under $175.
Let p represent the regular price of these t-shirt. Which of the following equations is correct?
\( \large 0.8p=\$8.73\) Hint: 80% of the regular price = $8.73. | |
\( \large \$8.73+0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice c. | |
\( \large 1.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice b. | |
\( \large p-0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: Subtract p from both sides of this equation, and you have -.2 x 8.73 =0. |
Question 35 |
The picture below shows identical circles drawn on a piece of paper. The rectangle represents an index card that is blocking your view of \( \dfrac{3}{5}\) of the circles on the paper. How many circles are covered by the rectangle?

4Hint: The card blocks more than half of the circles, so this number is too small. | |
5Hint: The card blocks more than half of the circles, so this number is too small. | |
8Hint: The card blocks more than half of the circles, so this number is too small. | |
12Hint: 2/5 of the circles or 8 circles are showing. Thus 4 circles represent 1/5 of the circles, and \(4 \times 5=20\) circles represent 5/5 or all the circles. Thus 12 circles are hidden. |
Question 36 |
Which of the numbers below is a fraction equivalent to \( 0.\bar{6}\)?
\( \large \dfrac{4}{6}\) Hint: \( 0.\bar{6}=\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{4}{6}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{5}\) Hint: This is equal to 0.6, without the repeating decimal. Answer is equivalent to choice c, which is another way to tell that it's wrong. | |
\( \large \dfrac{6}{10}\) Hint: This is equal to 0.6, without the repeating decimal. Answer is equivalent to choice b, which is another way to tell that it's wrong. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{6}\) Hint: This is less than a half, and \( 0.\bar{6}\) is greater than a half. |
Question 37 |
Below are front, side, and top views of a three-dimensional solid.
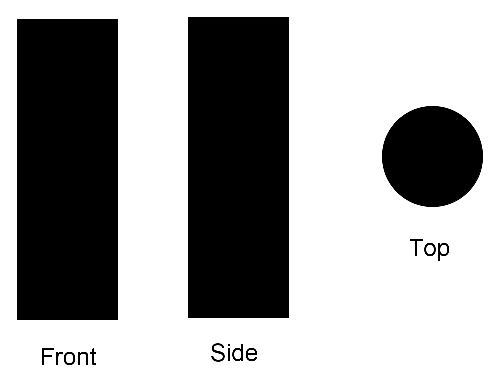
Which of the following could be the solid shown above?
A sphereHint: All views would be circles. | |
A cylinder | |
A coneHint: Two views would be triangles, not rectangles. | |
A pyramidHint: How would one view be a circle? |
Question 38 |
A biology class requires a lab fee, which is a whole number of dollars, and the same amount for all students. On Monday the instructor collected $70 in fees, on Tuesday she collected $126, and on Wednesday she collected $266. What is the largest possible amount the fee could be?
$2Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$7Hint: A possible fee, but not the largest possible fee. Check the other choices to see which are factors of all three numbers. | |
$14Hint: This is the greatest common factor of 70, 126, and 266. | |
$70Hint: Not a factor of 126 or 266, so couldn't be correct. |
Question 39 |
What is the mathematical name of the three-dimensional polyhedron depicted below?
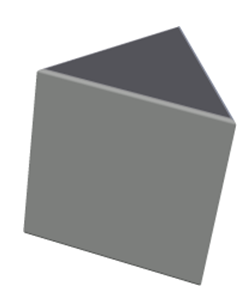
TetrahedronHint: All the faces of a tetrahedron are triangles. | |
Triangular PrismHint: A prism has two congruent, parallel bases, connected by parallelograms (since this is a right prism, the parallelograms are rectangles). | |
Triangular PyramidHint: A pyramid has one base, not two. | |
TrigonHint: A trigon is a triangle (this is not a common term). |
Question 40 |
What is the probability that two randomly selected people were born on the same day of the week? Assume that all days are equally probable.
\( \large \dfrac{1}{7}\) Hint: It doesn't matter what day the first person was born on. The probability that the second person will match is 1/7 (just designate one person the first and the other the second). Another way to look at it is that if you list the sample space of all possible pairs, e.g. (Wed, Sun), there are 49 such pairs, and 7 of them are repeats of the same day, and 7/49=1/7. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{14}\) Hint: What would be the sample space here? Ie, how would you list 14 things that you pick one from? | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{42}\) Hint: If you wrote the seven days of the week on pieces of paper and put the papers in a jar, this would be the probability that the first person picked Sunday and the second picked Monday from the jar -- not the same situation. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{49}\) Hint: This is the probability that they are both born on a particular day, e.g. Sunday. |
Question 41 |
A class is using base-ten block to represent numbers. A large cube represents 1000, a flat represents 100, a rod represents 10, and a little cube represents 1. Which of these is not a correct representation for 2,347?
23 flats, 4 rods, 7 little cubesHint: Be sure you read the question carefully: 2300+40+7=2347 | |
2 large cubes, 3 flats, 47 rodsHint: 2000+300+470 \( \neq\) 2347 | |
2 large cubes, 34 rods, 7 little cubesHint: Be sure you read the question carefully: 2000+340+7=2347 | |
2 large cubes, 3 flats, 4 rods, 7 little cubesHint: Be sure you read the question carefully: 2000+300+40+7=2347 |
Question 42 |
In March of 2012, 1 dollar was worth the same as 0.761 Euros, and 1 dollar was also worth the same as 83.03 Japanese Yen. Which of the expressions below gives the number of Yen that are worth 1 Euro?
\( \large {83}.0{3}\cdot 0.{761}\) Hint: This equation gives less than the number of yen per dollar, but 1 Euro is worth more than 1 dollar. | |
\( \large \dfrac{0.{761}}{{83}.0{3}}\) Hint: Number is way too small. | |
\( \large \dfrac{{83}.0{3}}{0.{761}}\) Hint: One strategy here is to use easier numbers, say 1 dollar = .5 Euros and 100 yen, then 1 Euro would be 200 Yen (change the numbers in the equations and see what works). Another is to use dimensional analysis: we want # yen per Euro, or yen/Euro = yen/dollar \(\times\) dollar/Euro = \(83.03 \times \dfrac {1}{0.761}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{0.{761}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{{83}.0{3}}\) Hint: Number is way too small. |
Question 43 |
How many lines of reflective symmetry and how many centers of rotational symmetry does the parallelogram depicted below have?

4 lines of reflective symmetry, 1 center of rotational symmetry.Hint: Try cutting out a shape like this one from paper, and fold where you think the lines of reflective symmetry are (or put a mirror there). Do things line up as you thought they would? | |
2 lines of reflective symmetry, 1 center of rotational symmetry.Hint: Try cutting out a shape like this one from paper, and fold where you think the lines of reflective symmetry are (or put a mirror there). Do things line up as you thought they would? | |
0 lines of reflective symmetry, 1 center of rotational symmetry.Hint: The intersection of the diagonals is a center of rotational symmetry. There are no lines of reflective symmetry, although many people get confused about this fact (best to play with hands on examples to get a feel). Just fyi, the letter S also has rotational, but not reflective symmetry, and it's one that kids often write backwards. | |
2 lines of reflective symmetry, 0 centers of rotational symmetry.Hint: Try cutting out a shape like this one from paper. Trace onto another sheet of paper. See if there's a way to rotate the cut out shape (less than a complete turn) so that it fits within the outlines again. |
Question 44 |
Solve for x: \(\large 4-\dfrac{2}{3}x=2x\)
\( \large x=3\) Hint: Try plugging x=3 into the equation. | |
\( \large x=-3\) Hint: Left side is positive, right side is negative when you plug this in for x. | |
\( \large x=\dfrac{3}{2}\) Hint: One way to solve: \(4=\dfrac{2}{3}x+2x\) \(=\dfrac{8}{3}x\).\(x=\dfrac{3 \times 4}{8}=\dfrac{3}{2}\). Another way is to just plug x=3/2 into the equation and see that each side equals 3 -- on a multiple choice test, you almost never have to actually solve for x. | |
\( \large x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\) Hint: Left side is positive, right side is negative when you plug this in for x. |
Question 45 |
Which of the following is equivalent to \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}?\)
\( \large \dfrac{7}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2}\) Hint: Addition and subtraction are of equal priority in the order of operations -- do them left to right. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{4}\) Hint: \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}+-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. |
|
List |
If you found a mistake or have comments on a particular question, please contact me (please copy and paste at least part of the question into the form, as the numbers change depending on how quizzes are displayed). General comments can be left here.