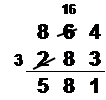Hints will display for most wrong answers; explanations for most right answers. You can attempt a question multiple times; it will only be scored correct if you get it right the first time.
I used the official objectives and sample test to construct these questions, but cannot promise that they accurately reflect what’s on the real test. Some of the sample questions were more convoluted than I could bear to write. See terms of use. See the MTEL Practice Test main page to view questions on a particular topic or to download paper practice tests.
MTEL General Curriculum Mathematics Practice
Question 1 |
The "houses" below are made of toothpicks and gum drops.
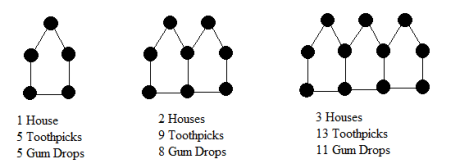
Which of the following does not represent the number of gumdrops in a row of h houses?
\( \large 2+3h\) Hint: Think of this as start with 2 gumdrops on the left wall, and then add 3 gumdrops for each house. | |
\( \large 5+3(h-1)\) Hint: Think of this as start with one house, and then add 3 gumdrops for each of the other h-1 houses. | |
\( \large h+(h+1)+(h+1)\) Hint: Look at the gumdrops in 3 rows: h gumdrops for the "rooftops," h+1 for the tops of the vertical walls, and h+1 for the floors. | |
\( \large 5+3h\) Hint: This one is not a correct equation (which makes it the correct answer!). Compare to choice A. One of them has to be wrong, as they differ by 3. |
Question 2 |
Which of the following is equivalent to \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}?\)
\( \large \dfrac{7}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2}\) Hint: Addition and subtraction are of equal priority in the order of operations -- do them left to right. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{4}\) Hint: \( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{2}{8}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}+-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{8}\)=\( \dfrac{3}{4}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{16}\) Hint: Multiplication comes before addition and subtraction in the order of operations. |
Question 3 |
The equation \( \large F=\frac{9}{5}C+32\) is used to convert a temperature measured in Celsius to the equivalent Farentheit temperature.
A patient's temperature increased by 1.5° Celcius. By how many degrees Fahrenheit did her temperature increase?
1.5°Hint: Celsius and Fahrenheit don't increase at the same rate. | |
1.8°Hint: That's how much the Fahrenheit temp increases when the Celsius temp goes up by 1 degree. | |
2.7°Hint: Each degree increase in Celsius corresponds to a \(\dfrac{9}{5}=1.8\) degree increase in Fahrenheit. Thus the increase is 1.8+0.9=2.7. | |
Not enough information.Hint: A linear equation has constant slope, which means that every increase of the same amount in one variable, gives a constant increase in the other variable. It doesn't matter what temperature the patient started out at. |
Question 4 |
Elena is going to use a calculator to check whether or not 267 is prime. She will pick certain divisors, and then find 267 divided by each, and see if she gets a whole number. If she never gets a whole number, then she's found a prime. Which numbers does Elena NEED to check before she can stop checking and be sure she has a prime?
All natural numbers from 2 to 266.Hint: She only needs to check primes -- checking the prime factors of any composite is enough to look for divisors. As a test taking strategy, the other three choices involve primes, so worth thinking about. | |
All primes from 2 to 266 .Hint: Remember, factors come in pairs (except for square root factors), so she would first find the smaller of the pair and wouldn't need to check the larger. | |
All primes from 2 to 133 .Hint: She doesn't need to check this high. Factors come in pairs, and something over 100 is going to be paired with something less than 3, so she will find that earlier. | |
All primes from \( \large 2\) to \( \large \sqrt{267}\).Hint: \(\sqrt{267} \times \sqrt{267}=267\). Any other pair of factors will have one factor less than \( \sqrt{267}\) and one greater, so she only needs to check up to \( \sqrt{267}\). |
Question 5 |
Use the expression below to answer the question that follows.
\( \large 3\times {{10}^{4}}+2.2\times {{10}^{2}}\)
Which of the following is closest to the expression above?
Five millionHint: Pay attention to the exponents. Adding 3 and 2 doesn't work because they have different place values. | |
Fifty thousandHint: Pay attention to the exponents. Adding 3 and 2 doesn't work because they have different place values. | |
Three millionHint: Don't add the exponents. | |
Thirty thousandHint: \( 3\times {{10}^{4}} = 30,000;\) the other term is much smaller and doesn't change the estimate. |
Question 6 |
The pattern below consists of a row of black squares surrounded by white squares.
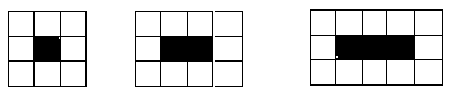
How many white squares would surround a row of 157 black squares?
314Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. | |
317Hint: Are there ever an odd number of white squares? | |
320Hint: One way to see this is that there are 6 tiles on the left and right ends, and the rest of the white tiles are twice the number of black tiles (there are many other ways to look at it too). | |
322Hint: Try your procedure on a smaller number that you can count to see where you made a mistake. |
Question 7 |
Which of the following is the equation of a linear function?
\( \large y={{x}^{2}}+2x+7\) Hint: This is a quadratic function. | |
\( \large y={{2}^{x}}\) Hint: This is an exponential function. | |
\( \large y=\dfrac{15}{x}\) Hint: This is an inverse function. | |
\( \large y=x+(x+4)\) Hint: This is a linear function, y=2x+4, it's graph is a straight line with slope 2 and y-intercept 4. |
Question 8 |
Here are some statements:
I) 5 is an integer II)\( -5 \) is an integer III) \(0\) is an integer
Which of the statements are true?
I only | |
I and II only | |
I and III only | |
I, II, and IIIHint: The integers are ...-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, .... |
Question 9 |
Which of the lists below is in order from least to greatest value?
\( \large -0.044,\quad -0.04,\quad 0.04,\quad 0.044\) Hint: These are easier to compare if you add trailing zeroes (this is finding a common denominator) -- all in thousandths, -0.044, -0.040,0 .040, 0.044. The middle two numbers, -0.040 and 0.040 can be modeled as owing 4 cents and having 4 cents. The outer two numbers are owing or having a bit more. | |
\( \large -0.04,\quad -0.044,\quad 0.044,\quad 0.04\) Hint: 0.04=0.040, which is less than 0.044. | |
\( \large -0.04,\quad -0.044,\quad 0.04,\quad 0.044\) Hint: -0.04=-0.040, which is greater than \(-0.044\). | |
\( \large -0.044,\quad -0.04,\quad 0.044,\quad 0.04\) Hint: 0.04=0.040, which is less than 0.044. |
Question 10 |
Which of the following sets of polygons can be assembled to form a pentagonal pyramid?
2 pentagons and 5 rectangles.Hint: These can be assembled to form a pentagonal prism, not a pentagonal pyramid. | |
1 square and 5 equilateral triangles.Hint: You need a pentagon for a pentagonal pyramid. | |
1 pentagon and 5 isosceles triangles. | |
1 pentagon and 10 isosceles triangles. |
Question 11 |
The letters A, and B represent digits (possibly equal) in the ten digit number x=1,438,152,A3B. For which values of A and B is x divisible by 12, but not by 9?
\( \large A = 0, B = 4\) Hint: Digits add to 31, so not divisible by 3, so not divisible by 12. | |
\( \large A = 7, B = 2\) Hint: Digits add to 36, so divisible by 9. | |
\( \large A = 0, B = 6\) Hint: Digits add to 33, divisible by 3, not 9. Last digits are 36, so divisible by 4, and hence by 12. | |
\( \large A = 4, B = 8\) Hint: Digits add to 39, divisible by 3, not 9. Last digits are 38, so not divisible by 4, so not divisible by 12. |
Question 12 |
The following story situations model \( 12\div 3\):
I) Jack has 12 cookies, which he wants to share equally between himself and two friends. How many cookies does each person get?
II) Trent has 12 cookies, which he wants to put into bags of 3 cookies each. How many bags can he make?
III) Cicely has $12. Cookies cost $3 each. How many cookies can she buy?
Which of these questions illustrate the same model of division, either partitive (partioning) or measurement (quotative)?
I and II | |
I and III | |
II and IIIHint: Problem I is partitive (or partitioning or sharing) -- we put 12 objects into 3 groups. Problems II and III are quotative (or measurement) -- we put 12 objects in groups of 3. | |
All three problems model the same meaning of division |
Question 13 |
Aya and Kendra want to estimate the height of a tree. On a sunny day, Aya measures Kendra's shadow as 3 meters long, and Kendra measures the tree's shadow as 15 meters long. Kendra is 1.5 meters tall. How tall is the tree?
7.5 metersHint: Here is a picture, note that the large and small right triangles are similar:  One way to do the problem is to note that there is a dilation (scale) factor of 5 on the shadows, so there must be that factor on the heights too. Another way is to note that the shadows are twice as long as the heights. | |
22.5 metersHint: Draw a picture. | |
30 metersHint: Draw a picture. | |
45 metersHint: Draw a picture. |
Question 14 |
Some children explored the diagonals in 2 x 2 squares on pages of a calendar (where all four squares have numbers in them). They conjectured that the sum of the diagonals is always equal; in the example below, 8+16=9+15.
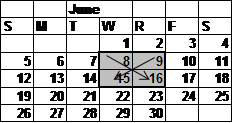
Which of the equations below could best be used to explain why the children's conjecture is correct?
\( \large 8x+16x=9x+15x\) Hint: What would x represent in this case? Make sure you can describe in words what x represents. | |
\( \large x+(x+2)=(x+1)+(x+1)\) Hint: What would x represent in this case? Make sure you can describe in words what x represents. | |
\( \large x+(x+8)=(x+1)+(x+7)\) Hint: x is the number in the top left square, x+8 is one below and to the right, x+1 is to the right of x, and x+7 is below x. | |
\( \large x+8+16=x+9+15\) Hint: What would x represent in this case? Make sure you can describe in words what x represents. |
Question 15 |
Kendra is trying to decide which fraction is greater, \( \dfrac{4}{7}\) or \( \dfrac{5}{8}\). Which of the following answers shows the best reasoning?
\( \dfrac{4}{7}\) is \( \dfrac{3}{7}\)away from 1, and \( \dfrac{5}{8}\) is \( \dfrac{3}{8}\)away from 1. Since eighth‘s are smaller than seventh‘s, \( \dfrac{5}{8}\) is closer to 1, and is the greater of the two fractions. | |
\( 7-4=3\) and \( 8-5=3\), so the fractions are equal.Hint: Not how to compare fractions. By this logic, 1/2 and 3/4 are equal, but 1/2 and 2/4 are not. | |
\( 4\times 8=32\) and \( 7\times 5=35\). Since \( 32<35\) , \( \dfrac{5}{8}<\dfrac{4}{7}\)Hint: Starts out as something that works, but the conclusion is wrong. 4/7 = 32/56 and 5/8 = 35/56. The cross multiplication gives the numerators, and 35/56 is bigger. | |
\( 4<5\) and \( 7<8\), so \( \dfrac{4}{7}<\dfrac{5}{8}\)Hint: Conclusion is correct, logic is wrong. With this reasoning, 1/2 would be less than 2/100,000. |
Question 16 |
The window glass below has the shape of a semi-circle on top of a square, where the side of the square has length x. It was cut from one piece of glass.
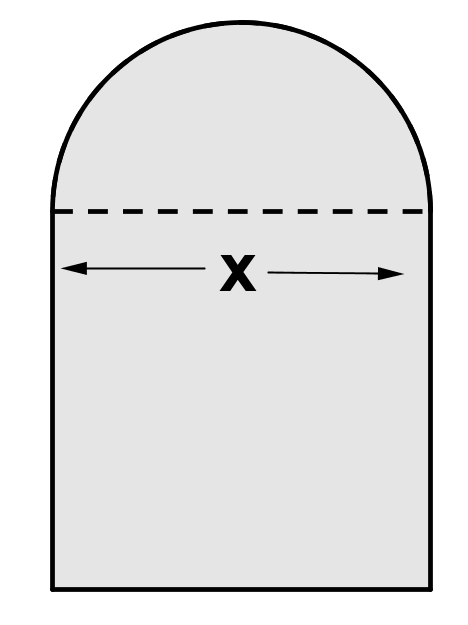
What is the perimeter of the window glass?
\( \large 3x+\dfrac{\pi x}{2}\) Hint: By definition, \(\pi\) is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter; thus the circumference is \(\pi d\). Since we have a semi-circle, its perimeter is \( \dfrac{1}{2} \pi x\). Only 3 sides of the square contribute to the perimeter. | |
\( \large 3x+2\pi x\) Hint: Make sure you know how to find the circumference of a circle. | |
\( \large 3x+\pi x\) Hint: Remember it's a semi-circle, not a circle. | |
\( \large 4x+2\pi x\) Hint: Only 3 sides of the square contribute to the perimeter. |
Question 17 |
Each individual cube that makes up the rectangular solid depicted below has 6 inch sides. What is the surface area of the solid in square feet?
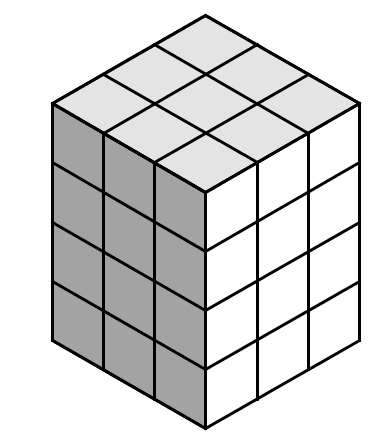
\( \large 11\text{ f}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\) Hint: Check your units and make sure you're using feet and inches consistently. | |
\( \large 16.5\text{ f}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\) Hint: Each square has surface area \(\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac {1}{2}=\dfrac {1}{4}\) sq feet. There are 9 squares on the top and bottom, and 12 on each of 4 sides, for a total of 66 squares. 66 squares \(\times \dfrac {1}{4}\) sq feet/square =16.5 sq feet. | |
\( \large 66\text{ f}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\) Hint: The area of each square is not 1. | |
\( \large 2376\text{ f}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\) Hint: Read the question more carefully -- the answer is supposed to be in sq feet, not sq inches.
|
Question 18 |
The Venn Diagram below gives data on the number of seniors, athletes, and vegetarians in the student body at a college:
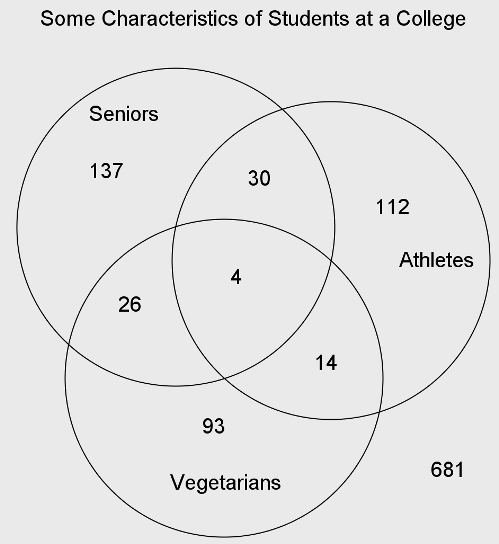
How many students at the college are seniors who are not vegetarians?
\( \large 137\) Hint: Doesn't include the senior athletes who are not vegetarians. | |
\( \large 167\) | |
\( \large 197\) Hint: That's all seniors, including vegetarians. | |
\( \large 279\) Hint: Includes all athletes who are not vegetarians, some of whom are not seniors. |
Question 19 |
Use the problem below to answer the question that follows:
T shirts are on sale for 20% off. Tasha paid $8.73 for a shirt. What is the regular price of the shirt? There is no tax on clothing purchases under $175.
Let p represent the regular price of these t-shirt. Which of the following equations is correct?
\( \large 0.8p=\$8.73\) Hint: 80% of the regular price = $8.73. | |
\( \large \$8.73+0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice c. | |
\( \large 1.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: The 20% off was off of the ORIGINAL price, not off the $8.73 (a lot of people make this mistake). Plus this is the same equation as in choice b. | |
\( \large p-0.2*\$8.73=p\) Hint: Subtract p from both sides of this equation, and you have -.2 x 8.73 =0. |
Question 20 |
Below are four inputs and outputs for a function machine representing the function A:
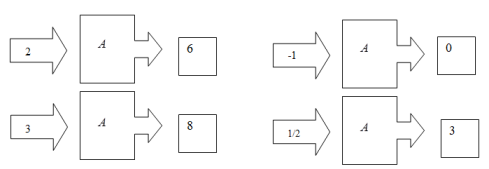
Which of the following equations could also represent A for the values shown?
\( \large A(n)=n+4\) Hint: For a question like this, you don't have to find the equation yourself, you can just try plugging the function machine inputs into the equation, and see if any values come out wrong. With this equation n= -1 would output 3, not 0 as the machine does. | |
\( \large A(n)=n+2\) Hint: For a question like this, you don't have to find the equation yourself, you can just try plugging the function machine inputs into the equation, and see if any values come out wrong. With this equation n= 2 would output 4, not 6 as the machine does. | |
\( \large A(n)=2n+2\) Hint: Simply plug in each of the four function machine input values, and see that the equation produces the correct output, e.g. A(2)=6, A(-1)=0, etc. | |
\( \large A(n)=2\left( n+2 \right)\) Hint: For a question like this, you don't have to find the equation yourself, you can just try plugging the function machine inputs into the equation, and see if any values come out wrong. With this equation n= 2 would output 8, not 6 as the machine does. |
Question 21 |
The least common multiple of 60 and N is 1260. Which of the following could be the prime factorization of N?
\( \large2\cdot 5\cdot 7\) Hint: 1260 is divisible by 9 and 60 is not, so N must be divisible by 9 for 1260 to be the LCM. | |
\( \large{{2}^{3}}\cdot {{3}^{2}}\cdot 5 \cdot 7\) Hint: 1260 is not divisible by 8, so it isn't a multiple of this N. | |
\( \large3 \cdot 5 \cdot 7\) Hint: 1260 is divisible by 9 and 60 is not, so N must be divisible by 9 for 1260 to be the LCM. | |
\( \large{{3}^{2}}\cdot 5\cdot 7\) Hint: \(1260=2^2 \cdot 3^2 \cdot 5 \cdot 7\) and \(60=2^2 \cdot 3 \cdot 5\). In order for 1260 to be the LCM, N has to be a multiple of \(3^2\) and of 7 (because 60 is not a multiple of either of these). N also cannot introduce a factor that would require the LCM to be larger (as in choice b). |
Question 22 |
Taxicab fares in Boston (Spring 2012) are $2.60 for the first \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile or less and $0.40 for each \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) of a mile after that.
Let d represent the distance a passenger travels in miles (with \(d>\dfrac{1}{7}\)). Which of the following expressions represents the total fare?
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40d\) Hint: It's 40 cents for 1/7 of a mile, not per mile. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$0.40\dfrac{d}{7}\) Hint: According to this equation, going 7 miles would cost $3; does that make sense? | |
\( \large \$2.20+\$2.80d\) Hint: You can think of the fare as $2.20 to enter the cab, and then $0.40 for each 1/7 of a mile, including the first 1/7 of a mile (or $2.80 per mile).
Alternatively, you pay $2.60 for the first 1/7 of a mile, and then $2.80 per mile for d-1/7 miles. The total is 2.60+2.80(d-1/7) = 2.60+ 2.80d -.40 = 2.20+2.80d. | |
\( \large \$2.60+\$2.80d\) Hint: Don't count the first 1/7 of a mile twice. |
Question 23 |
| I. \(\large \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}\) | II. \( \large .400000\) | III. \(\large\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}\) |
| IV. \( \large 40\% \) | V. \( \large 0.25 \) | VI. \(\large\dfrac{14}{35}\) |
Which of the lists below includes all of the above expressions that are equivalent to \( \dfrac{2}{5}\)?
I, III, V, VIHint: I and V are not at all how fractions and decimals work. | |
III, VIHint: These are right, but there are more. | |
II, III, VIHint: These are right, but there are more. | |
II, III, IV, VI |
Question 24 |
In the triangle below, \(\overline{AC}\cong \overline{AD}\cong \overline{DE}\) and \(m\angle CAD=100{}^\circ \). What is \(m\angle DAE\)?
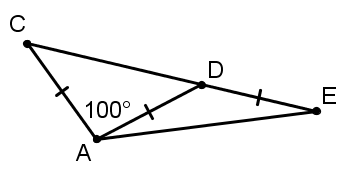
\( \large 20{}^\circ \) Hint: Angles ACD and ADC are congruent since they are base angles of an isosceles triangle. Since the angles of a triangle sum to 180, they sum to 80, and they are 40 deg each. Thus angle ADE is 140 deg, since it makes a straight line with angle ADC. Angles DAE and DEA are base angles of an isosceles triangle and thus congruent-- they sum to 40 deg, so are 20 deg each. | |
\( \large 25{}^\circ \) Hint: If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then it's isosceles, and the base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal. | |
\( \large 30{}^\circ \) Hint: If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then it's isosceles, and the base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal. | |
\( \large 40{}^\circ \) Hint: Make sure you're calculating the correct angle. |
Question 25 |
A publisher prints a series of books with covers made of identical material and using the same thickness of paper for each page. The covers of the book together are 0.4 cm thick, and 125 pieces of the paper used together are 1 cm thick.
The publisher uses a linear function to determine the total thickness, T(n) of a book made with n sheets of paper. What are the slope and intercept of T(n)?
Intercept = 0.4 cm, Slope = 125 cm/pageHint: This would mean that each page of the book was 125 cm thick. | |
Intercept =0.4 cm, Slope = \(\dfrac{1}{125}\)cm/pageHint: The intercept is how thick the book would be with no pages in it. The slope is how much 1 extra page adds to the thickness of the book. | |
Intercept = 125 cm, Slope = 0.4 cmHint: This would mean that with no pages in the book, it would be 125 cm thick. | |
Intercept = \(\dfrac{1}{125}\)cm, Slope = 0.4 pages/cmHint: This would mean that each new page of the book made it 0.4 cm thicker. |
Question 26 |
The first histogram shows the average life expectancies for women in different countries in Africa in 1998; the second histogram gives similar data for Europe:
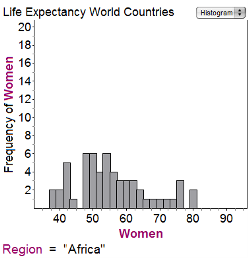
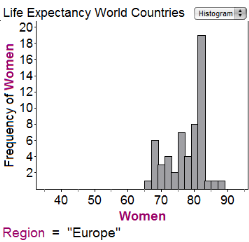
How much bigger is the range of the data for Africa than the range of the data for Europe?
0 yearsHint: Range is the maximum life expectancy minus the minimum life expectancy. | |
12 yearsHint: Are you subtracting frequencies? Range is about values of the data, not frequency. | |
18 yearsHint: It's a little hard to read the graph, but it doesn't matter if you're consistent. It looks like the range for Africa is 80-38= 42 years and for Europe is 88-64 = 24; 42-24=18. | |
42 yearsHint: Read the question more carefully. |
Question 27 |
Below is a portion of a number line.
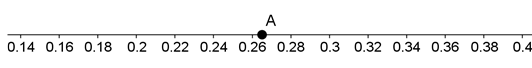
Point A is one-quarter of the distance from 0.26 to 0.28. What number is represented by point A?
\( \large0.26\) Hint: Please reread the question. | |
\( \large0.2625\) Hint: This is one-quarter of the distance between 0.26 and 0.27, which is not what the question asked. | |
\( \large0.265\) | |
\( \large0.27\) Hint: Please read the question more carefully. This answer would be correct if Point A were halfway between the tick marks, but it's not. |
Question 28 |
Which of the graphs below represent functions?
I.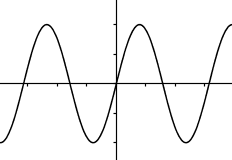 II.
II. 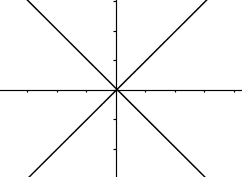 III.
III. 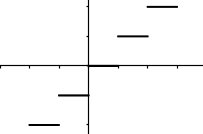 IV.
IV. 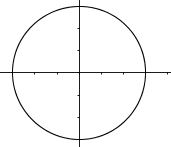
I and IV only.Hint: There are vertical lines that go through 2 points in IV . | |
I and III only.Hint: Even though III is not continuous, it's still a function (assuming that vertical lines between the "steps" do not go through 2 points). | |
II and III only.Hint: Learn about the vertical line test. | |
I, II, and IV only.Hint: There are vertical lines that go through 2 points in II. |
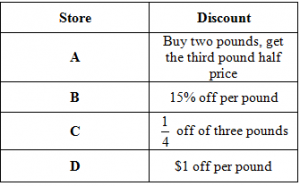
Question 29 |
Use the table below to answer the question that follows:
Gordon wants to buy three pounds of nuts. Each of the stores above ordinarily sells the nuts for $4.99 a pound, but is offering a discount this week. At which store can he buy the nuts for the least amount of money?
Store AHint: This would save about $2.50. You can quickly see that D saves more. | |
Store BHint: This saves 15% and C saves 25%. | |
Store C | |
Store DHint: This is about 20% off, which is less of a discount than C. |
Question 30 |
Which of the following is equivalent to
\( \large A-B+C\div D\times E\)?
\( \large A-B-\dfrac{C}{DE}
\) Hint: In the order of operations, multiplication and division have the same priority, so do them left to right; same with addition and subtraction. | |
\( \large A-B+\dfrac{CE}{D}\) Hint: In practice, you're better off using parentheses than writing an expression like the one in the question. The PEMDAS acronym that many people memorize is misleading. Multiplication and division have equal priority and are done left to right. They have higher priority than addition and subtraction. Addition and subtraction also have equal priority and are done left to right. | |
\( \large \dfrac{AE-BE+CE}{D}\) Hint: Use order of operations, don't just compute left to right. | |
\( \large A-B+\dfrac{C}{DE}\) Hint: In the order of operations, multiplication and division have the same priority, so do them left to right |
Question 31 |
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows:
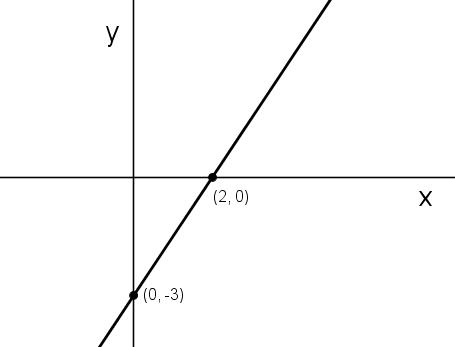
The graph above represents the equation \( \large 3x+Ay=B\), where A and B are integers. What are the values of A and B?
\( \large A = -2, B= 6\) Hint: Plug in (2,0) to get B=6, then plug in (0,-3) to get A=-2. | |
\( \large A = 2, B = 6\) Hint: Try plugging (0,-3) into this equation. | |
\( \large A = -1.5, B=-3\) Hint: The problem said that A and B were integers and -1.5 is not an integer. Don't try to use slope-intercept form. | |
\( \large A = 2, B = -3\) Hint: Try plugging (2,0) into this equation. |
Question 32 |
The polygon depicted below is drawn on dot paper, with the dots spaced 1 unit apart. What is the perimeter of the polygon?

\( \large 18+\sqrt{2} \text{ units}\) Hint: Be careful with the Pythagorean Theorem. | |
\( \large 18+2\sqrt{2}\text{ units}\) Hint: There are 13 horizontal or vertical 1 unit segments. The longer diagonal is the hypotenuse of a 3-4-5 right triangle, so its length is 5 units. The shorter diagonal is the hypotenuse of a 45-45-90 right triangle with side 2, so its hypotenuse has length \(2 \sqrt{2}\). | |
\( \large 18 \text{ units}
\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the diagonal segments. | |
\( \large 20 \text{ units}\) Hint: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the diagonal segments. |
Question 33 |
In March of 2012, 1 dollar was worth the same as 0.761 Euros, and 1 dollar was also worth the same as 83.03 Japanese Yen. Which of the expressions below gives the number of Yen that are worth 1 Euro?
\( \large {83}.0{3}\cdot 0.{761}\) Hint: This equation gives less than the number of yen per dollar, but 1 Euro is worth more than 1 dollar. | |
\( \large \dfrac{0.{761}}{{83}.0{3}}\) Hint: Number is way too small. | |
\( \large \dfrac{{83}.0{3}}{0.{761}}\) Hint: One strategy here is to use easier numbers, say 1 dollar = .5 Euros and 100 yen, then 1 Euro would be 200 Yen (change the numbers in the equations and see what works). Another is to use dimensional analysis: we want # yen per Euro, or yen/Euro = yen/dollar \(\times\) dollar/Euro = \(83.03 \times \dfrac {1}{0.761}\) | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{0.{761}}\cdot \dfrac{1}{{83}.0{3}}\) Hint: Number is way too small. |
Question 34 |
Which of the numbers below is not equivalent to 4%?
\( \large \dfrac{1}{25}\) Hint: 1/25=4/100, so this is equal to 4% (be sure you read the question correctly). | |
\( \large \dfrac{4}{100}\) Hint: 4/100=4% (be sure you read the question correctly). | |
\( \large 0.4\) Hint: 0.4=40% so this is not equal to 4% | |
\( \large 0.04\) Hint: 0.04=4/100, so this is equal to 4% (be sure you read the question correctly). |
Question 35 |
The student used a method that worked for this problem and can be generalized to any subtraction problem.Hint: Note that this algorithm is taught as the "standard" algorithm in much of Europe (it's where the term "borrowing" came from -- you borrow on top and "pay back" on the bottom). | |
The student used a method that worked for this problem and that will work for any subtraction problem that only requires one regrouping; it will not work if more regrouping is required.Hint: Try some more examples. | |
The student used a method that worked for this problem and will work for all three-digit subtraction problems, but will not work for larger problems.Hint: Try some more examples. | |
The student used a method that does not work. The student made two mistakes that cancelled each other out and was lucky to get the right answer for this problem.Hint: Remember, there are many ways to do subtraction; there is no one "right" algorithm. |
Question 36 |
P is a prime number that divides 240. Which of the following must be true?
P divides 30Hint: 2, 3, and 5 are the prime factors of 240, and all divide 30. | |
P divides 48Hint: P=5 doesn't work. | |
P divides 75Hint: P=2 doesn't work. | |
P divides 80Hint: P=3 doesn't work. |
Question 37 |
A class is using base-ten block to represent numbers. A large cube represents 1000, a flat represents 100, a rod represents 10, and a little cube represents 1. Which of these is not a correct representation for 2,347?
23 flats, 4 rods, 7 little cubesHint: Be sure you read the question carefully: 2300+40+7=2347 | |
2 large cubes, 3 flats, 47 rodsHint: 2000+300+470 \( \neq\) 2347 | |
2 large cubes, 34 rods, 7 little cubesHint: Be sure you read the question carefully: 2000+340+7=2347 | |
2 large cubes, 3 flats, 4 rods, 7 little cubesHint: Be sure you read the question carefully: 2000+300+40+7=2347 |
Question 38 |
M is a multiple of 26. Which of the following cannot be true?
M is odd.Hint: All multiples of 26 are also multiples of 2, so they must be even. | |
M is a multiple of 3.Hint: 3 x 26 is a multiple of both 3 and 26. | |
M is 26.Hint: 1 x 26 is a multiple of 26. | |
M is 0.Hint: 0 x 26 is a multiple of 26. |
Question 39 |
The speed of sound in dry air at 68 degrees F is 343.2 meters per second. Which of the expressions below could be used to compute the number of kilometers that a sound wave travels in 10 minutes (in dry air at 68 degrees F)?
\( \large 343.2\times 60\times 10\) Hint: In kilometers, not meters. | |
\( \large 343.2\times 60\times 10\times \dfrac{1}{1000}\) Hint: Units are meters/sec \(\times\) seconds/minute \(\times\) minutes \(\times\) kilometers/meter, and the answer is in kilometers. | |
\( \large 343.2\times \dfrac{1}{60}\times 10\) Hint: Include units and make sure answer is in kilometers. | |
\( \large 343.2\times \dfrac{1}{60}\times 10\times \dfrac{1}{1000}\) Hint: Include units and make sure answer is in kilometers. |
Question 40 |
Which of the following is equal to one million three hundred thousand?
\(\large1.3\times {{10}^{6}}\)
| |
\(\large1.3\times {{10}^{9}}\)
Hint: That's one billion three hundred million. | |
\(\large1.03\times {{10}^{6}}\)
Hint: That's one million thirty thousand. | |
\(\large1.03\times {{10}^{9}}\) Hint: That's one billion thirty million |
Question 41 |
On a map the distance from Boston to Detroit is 6 cm, and these two cities are 702 miles away from each other. Assuming the scale of the map is the same throughout, which answer below is closest to the distance between Boston and San Francisco on the map, given that they are 2,708 miles away from each other?
21 cmHint: How many miles would correspond to 24 cm on the map? Try adjusting from there. | |
22 cmHint: How many miles would correspond to 24 cm on the map? Try adjusting from there. | |
23 cmHint: One way to solve this without a calculator is to note that 4 groups of 6 cm is 2808 miles, which is 100 miles too much. Then 100 miles would be about 1/7 th of 6 cm, or about 1 cm less than 24 cm. | |
24 cmHint: 4 groups of 6 cm is over 2800 miles on the map, which is too much. |
Question 42 |
A sales companies pays its representatives $2 for each item sold, plus 40% of the price of the item. The rest of the money that the representatives collect goes to the company. All transactions are in cash, and all items cost $4 or more. If the price of an item in dollars is p, which expression represents the amount of money the company collects when the item is sold?
\( \large \dfrac{3}{5}p-2\) Hint: The company gets 3/5=60% of the price, minus the $2 per item. | |
\( \large \dfrac{3}{5}\left( p-2 \right)\) Hint: This is sensible, but not what the problem states. | |
\( \large \dfrac{2}{5}p+2\) Hint: The company pays the extra $2; it doesn't collect it. | |
\( \large \dfrac{2}{5}p-2\) Hint: This has the company getting 2/5 = 40% of the price of each item, but that's what the representative gets. |
Question 43 |
Which of the lists below is in order from least to greatest value?
\( \large \dfrac{1}{2},\quad \dfrac{1}{3},\quad \dfrac{1}{4},\quad \dfrac{1}{5}\) Hint: This is ordered from greatest to least. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{3},\quad \dfrac{2}{7},\quad \dfrac{3}{8},\quad \dfrac{4}{11}\) Hint: 1/3 = 2/6 is bigger than 2/7. | |
\( \large \dfrac{1}{4},\quad \dfrac{2}{5},\quad \dfrac{2}{3},\quad \dfrac{4}{5}\) Hint: One way to look at this: 1/4 and 2/5 are both less than 1/2, and 2/3 and 4/5 are both greater than 1/2. 1/4 is 25% and 2/5 is 40%, so 2/5 is greater. The distance from 2/3 to 1 is 1/3 and from 4/5 to 1 is 1/5, and 1/5 is less than 1/3, so 4/5 is bigger. | |
\( \large \dfrac{7}{8},\quad \dfrac{6}{7},\quad \dfrac{5}{6},\quad \dfrac{4}{5}\) Hint: This is in order from greatest to least. |
Question 44 |
What set of transformations will transform the leftmost image into the rightmost image?
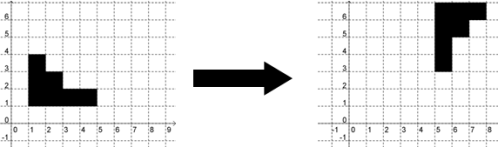
A 90 degree clockwise rotation about (2,1) followed by a translation of two units to the right.Hint: Part of the figure would move below the x-axis with these transformations. | |
A translation 3 units up, followed by a reflection about the line y=x.Hint: See what happens to the point (5,1) under this set of transformations. | |
A 90 degree clockwise rotation about (5,1), followed by a translation of 2 units up. | |
A 90 degree clockwise rotation about (2,1) followed by a translation of 2 units to the right.Hint: See what happens to the point (3,3) under this set of transformations. |
Question 45 |
A family on vacation drove the first 200 miles in 4 hours and the second 200 miles in 5 hours. Which expression below gives their average speed for the entire trip?
\( \large \dfrac{200+200}{4+5}\) Hint: Average speed is total distance divided by total time. | |
\( \large \left( \dfrac{200}{4}+\dfrac{200}{5} \right)\div 2\) Hint: This seems logical, but the problem is that it weights the first 4 hours and the second 5 hours equally, when each hour should get the same weight in computing the average speed. | |
\( \large \dfrac{200}{4}+\dfrac{200}{5} \) Hint: This would be an average of 90 miles per hour! | |
\( \large \dfrac{400}{4}+\dfrac{400}{5} \) Hint: This would be an average of 180 miles per hour! Even a family of race car drivers probably doesn't have that average speed on a vacation! |
|
List |
If you found a mistake or have comments on a particular question, please contact me (please copy and paste at least part of the question into the form, as the numbers change depending on how quizzes are displayed). General comments can be left here.